FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Join the Fabric FabCon Global Hackathon—running virtually through Nov 3. Open to all skill levels. $10,000 in prizes! Register now.
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Power Query
- Re: the number of times unpivoting a row
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
the number of times unpivoting a row
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @RichaBansal
With that exact data no, but if the Start and End Columns were formated as dates, then yes.
- Add a custom column to create month amount between dates
Date.Year([End])*12+Date.Month([End])-Date.Year([Start])*12-Date.Month([Start])
- Create a column to calculate Monthly Amount
[Amount]/ [Custom]
- Create another column called "Intervals"
List.Numbers(1,[Custom])
- Then add another to create the months
Date.StartOfMonth(
Date.AddMonths(
[Start],
[Intervals] -1
)
))
This should help
Joe
If you found my answer helpful and it solved your issue, please accept as solution
Proud to be a Super User! |  |
Date tables help! Learn more
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I think I missed a step. You will need to expand the list to new rows before adding the last step
Proud to be a Super User! |  |
Date tables help! Learn more
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @RichaBansal
With that exact data no, but if the Start and End Columns were formated as dates, then yes.
- Add a custom column to create month amount between dates
Date.Year([End])*12+Date.Month([End])-Date.Year([Start])*12-Date.Month([Start])
- Create a column to calculate Monthly Amount
[Amount]/ [Custom]
- Create another column called "Intervals"
List.Numbers(1,[Custom])
- Then add another to create the months
Date.StartOfMonth(
Date.AddMonths(
[Start],
[Intervals] -1
)
))
This should help
Joe
If you found my answer helpful and it solved your issue, please accept as solution
Proud to be a Super User! |  |
Date tables help! Learn more
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
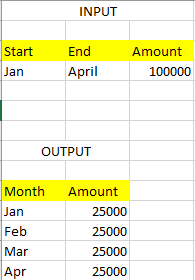
Hi Joe,
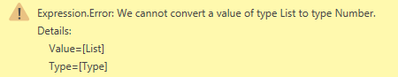
The start and end are dates. I got the list of numbers, but the Last column shows error.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I think I missed a step. You will need to expand the list to new rows before adding the last step
Proud to be a Super User! |  |
Date tables help! Learn more
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
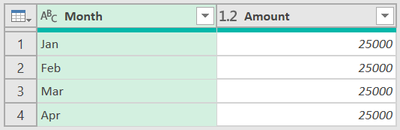
Worked like a charm 🙂
Thank you Joe. Have a pleasant day.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
This will work only in case when Start and End are defined as dates. @RichaBansal, let us know if input Start and End are dates or just text "Jan" and "April"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@RichaBansal, in case you have input stored as text, try this:
Result:
let
Source = Table.FromRows(Json.Document(Binary.Decompress(Binary.FromText("i45W8krMU9JRciwoyswB0oYGIKAUGwsA", BinaryEncoding.Base64), Compression.Deflate)), let _t = ((type nullable text) meta [Serialized.Text = true]) in type table [Start = _t, End = _t, Amount = _t]),
Transformed = Table.TransformColumns(Source, {
{"Start", each Date.Month(Date.FromText("2024" & Text.Start(_,3) & "01", [Format="yyyyMMMdd", Culture="en-US"])), Int64.Type},
{"End", each Date.Month(Date.FromText("2024" & Text.Start(_,3) & "01", [Format="yyyyMMMdd", Culture="en-US"])), Int64.Type},
{"Amount", Number.From, type number}
}),
Ad_FinalTable = Table.AddColumn(Transformed, "FinalTable", each
[ a = [Amount] / ([End]-[Start]+1),
b = List.Transform({[Start]..[End]}, (x)=> Date.ToText(#date(2024,x,1), "MMM", "en-US")),
c = Table.FromColumns({ b, List.Repeat({a}, List.Count(b)) }, type table[Month=text, Amount=number])
][c], type table),
FinalTable = Table.Combine(Ad_FinalTable[FinalTable])
in
FinalTable