FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Vote for your favorite vizzies from the Power BI Dataviz World Championship submissions. Vote now!
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Power Query
- Split a .csv with multiple tables into multiple qu...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Split a .csv with multiple tables into multiple queries
Hi there. I am working with a .csv file produced by a proprietary application that includes 4 different tables all jammed together into a single file. The tables themselves are different to each other and are separated by a single blank row.
| Header 1 | Header 2 | Header 3 | Header 4 |
| Value 1 | Value 2 | Value 3 | Value 4 |
| Header 1 | Header 2 | Header 3 | Header 4 |
| Value 1 | Value 2 | Value 3 | Value 4 |
| Header 1 | Header 2 | Header 3 | Header 4 |
| Value 1 | Value 2 | Value 3 | Value 4 |
| Header 1 | Header 2 | Header 3 | Header 4 |
| Value 1 | Value 2 | Value 3 | Value 4 |
They contain different information which I would like to interrogate separately. Currently, I take the .csv and manually separate into four .csvs which I then pull into Power BI separately and interrogate as 4 separate queries.
Is there a way for me to import the .csv into Power BI and then split the four tables into four queries? The clear delimiter here is the blank row that separates each table from each other.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
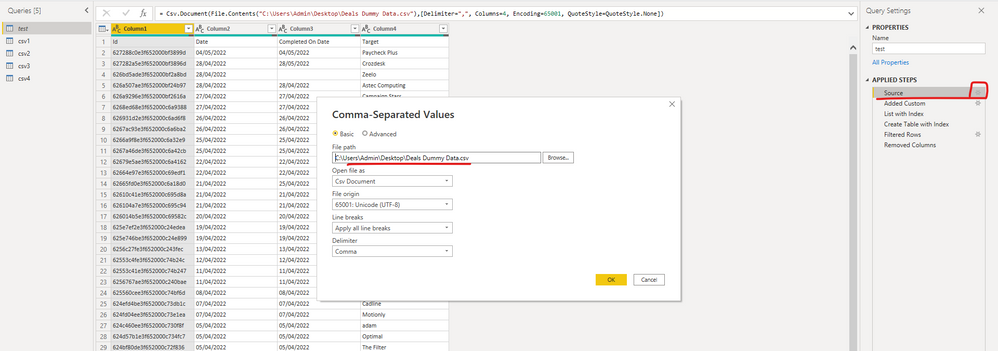
1. Import your csv and have following code for primary file (C:\test.csv should be replaced with your csv file path)
let
Source = Csv.Document(File.Contents("C:\test.csv"),[Delimiter=",", Columns=4, Encoding=65001, QuoteStyle=QuoteStyle.None]),
#"Added Custom" = Table.AddColumn(Source, "IsBlank", each List.IsEmpty(List.RemoveItems(Record.ToList(_),{""}))),
#"List with Index" = List.Generate(()=>[x=0,i=0], each [i]<Table.RowCount(#"Added Custom"), each [i=[i]+1, x=(if #"Added Custom"[IsBlank]{i}=true then [x]+1 else [x])], each [x]),
#"Create Table with Index" = Table.FromColumns(Table.ToColumns(#"Added Custom") & {#"List with Index"},Table.ColumnNames(#"Added Custom")&{"Index"}),
#"Filtered Rows" = Table.SelectRows(#"Create Table with Index", each ([IsBlank] = false)),
#"Removed Columns" = Table.RemoveColumns(#"Filtered Rows",{"IsBlank"})
in
#"Removed Columns"2. Right click on this query in left pane and uncheck Enable load as this file need not be loaded into your report.
3. Right click on this query and Reference. Create overall 4 references. Rename them as csv1, csv2, csv3 and csv4 or whatever name you like.
4. In csv1, filter it on Index 0, in csv2, filter on 1, in csv3, filter on 2 and in csv4, filter on 3. Delete Index columns from there.
5. Promote headers in all these 4 queries and do a Detect data type for entire table.
The solution file as well as test.csv used in this can be downloaded from - https://1drv.ms/u/s!Akd5y6ruJhvhuWwDHySKxd-kYc0-?e=scwGxK
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi there Vijay,
Thanks for the quick reply and the solution. I should have included two bits of information:
1) The data I am using is not static. It is used in a recurring piece of analysis and as such, the original .csv will be downloaded regularly (usually weekly) with the most up-to-date information. I want to get the dashboard to a situation where I just need to download the .csv, move it into the correct folder and overwrite the existing file, then click refresh on Power BI to get the most up-to-date stats. Will this solution work with that?
2) Each table has a different number of columns. Two have 91 columns, one has 21, and one has 126. This may change in the future.
Do either of these factors affect the code you have shared? Here is a dummy version of the .csv if that helps.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Iarampatta ,
@Iarampatta ‘s workaround is good.
Download his file and open it. Go to the Power Query Editor, and then click the gear next to Source in the main table and replace the source file with yours.
Then remove the 'Change Type' step, and you can see the data after removing it.
Best Regards,
Stephen Tao
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
1. Import your csv and have following code for primary file (C:\test.csv should be replaced with your csv file path)
let
Source = Csv.Document(File.Contents("C:\test.csv"),[Delimiter=",", Columns=4, Encoding=65001, QuoteStyle=QuoteStyle.None]),
#"Added Custom" = Table.AddColumn(Source, "IsBlank", each List.IsEmpty(List.RemoveItems(Record.ToList(_),{""}))),
#"List with Index" = List.Generate(()=>[x=0,i=0], each [i]<Table.RowCount(#"Added Custom"), each [i=[i]+1, x=(if #"Added Custom"[IsBlank]{i}=true then [x]+1 else [x])], each [x]),
#"Create Table with Index" = Table.FromColumns(Table.ToColumns(#"Added Custom") & {#"List with Index"},Table.ColumnNames(#"Added Custom")&{"Index"}),
#"Filtered Rows" = Table.SelectRows(#"Create Table with Index", each ([IsBlank] = false)),
#"Removed Columns" = Table.RemoveColumns(#"Filtered Rows",{"IsBlank"})
in
#"Removed Columns"2. Right click on this query in left pane and uncheck Enable load as this file need not be loaded into your report.
3. Right click on this query and Reference. Create overall 4 references. Rename them as csv1, csv2, csv3 and csv4 or whatever name you like.
4. In csv1, filter it on Index 0, in csv2, filter on 1, in csv3, filter on 2 and in csv4, filter on 3. Delete Index columns from there.
5. Promote headers in all these 4 queries and do a Detect data type for entire table.
The solution file as well as test.csv used in this can be downloaded from - https://1drv.ms/u/s!Akd5y6ruJhvhuWwDHySKxd-kYc0-?e=scwGxK
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
Vote for your favorite vizzies from the Power BI World Championship submissions!

Join our Community Sticker Challenge 2026
If you love stickers, then you will definitely want to check out our Community Sticker Challenge!

Power BI Monthly Update - January 2026
Check out the January 2026 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 13 | |
| 11 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 |