FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now! Learn more
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Re: AllSelected In A Summarize Table
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
AllSelected In A Summarize Table
I have a table of Months, Salesperson and Sales.
I want to create a summary table of the median sales total for each month.
I am using the following formula
FilteredValues = Summarize(AllSelected(AllSales), AllSales[Month], "Median Monthly Sales", Median(AllSales[Units]))
But when I filter on a subset of the sales people the table remains static and gives the total for all sales people.
How do I create a summary table that calculates median based on the selections only?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey,
as far as I understand your question I would create a measure like so
Median Monthly Sales =
CALCULATE(
Median('AllSales'[Units]),
ALL('AllSales'[Month)
)
Did I answer your question? Mark my post as a solution, this will help others!
Proud to be a Super User!
I accept Kudos 😉
Hamburg, Germany
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks Tom, but that isn't giving me what i need.
If we use the example below
Month SalesPerson Units
Jan ID0001 1000
Jan ID0002 2000
Jan ID0003 3000
Jan ID0004 4000
Jan ID0005 5000
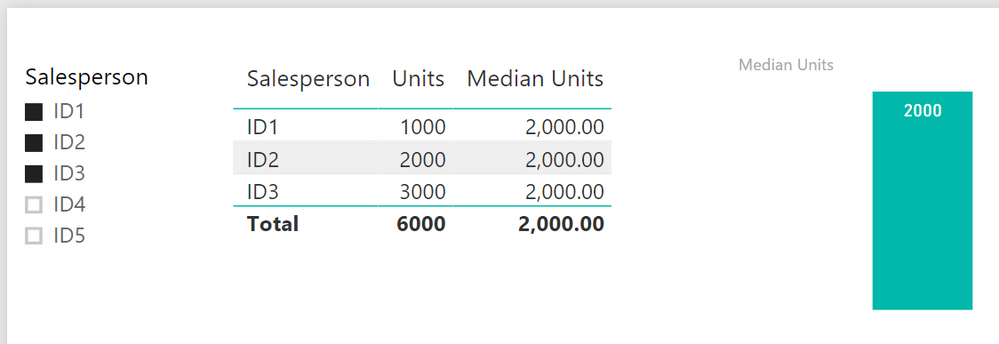
I want to create a summary table that gives a median of 3000 when there is no filter on SalesPerson but gives a Median of 2000 if I am filtering on ID0001, ID0002 & ID0003 only.
Is that possible to do?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey,
it's possible 🙂
my table is called 'sampleALLSELECTED'
Median Units =
CALCULATE(
MEDIAN('sampleALLSELECTED'[Units]),
ALLSELECTED(sampleALLSELECTED[Salesperson])
) And you will get this
Hope this will help
Did I answer your question? Mark my post as a solution, this will help others!
Proud to be a Super User!
I accept Kudos 😉
Hamburg, Germany
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Tom,
Thanks but that is not quite what I am trying to achieve.
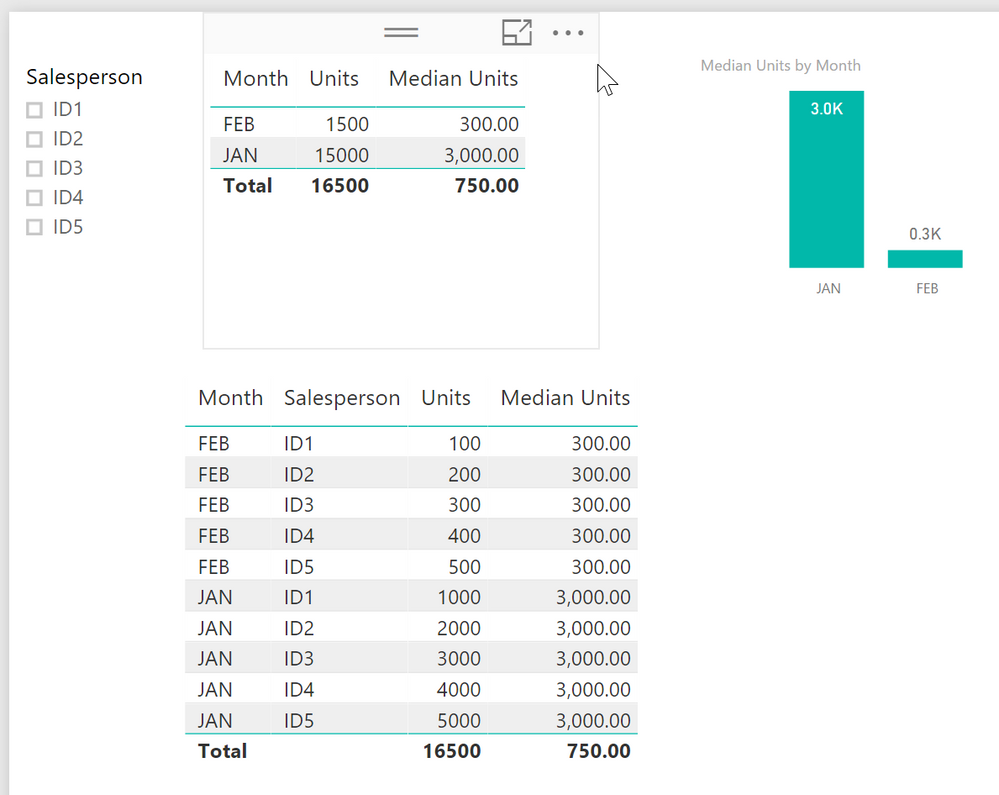
I need a table which has one row per month and gives the mendian for each month based on the selections, so I am trying to do this as a Summarize table. Is there a way to create a summarize table that updates according to selections? Using AllSelected doesn't seem to have any effect.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey,
you can achieve what you want by using Month the Measure in a table vis
The second table shows all the data.
You can't use a calculated table / virtual table, as a source for a visual, due to the fact that it is static (reflecting the moment (current selections) when you calculate the table.
For this reason, you have to use a measure, unfortunately, but currently I can't see why a measure is not "good enough"
Did I answer your question? Mark my post as a solution, this will help others!
Proud to be a Super User!
I accept Kudos 😉
Hamburg, Germany
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now!

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 38 | |
| 36 | |
| 33 | |
| 32 | |
| 29 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 129 | |
| 88 | |
| 79 | |
| 68 | |
| 63 |