New Offer! Become a Certified Fabric Data Engineer
Check your eligibility for this 50% exam voucher offer and join us for free live learning sessions to get prepared for Exam DP-700.
Get StartedJoin us at the 2025 Microsoft Fabric Community Conference. March 31 - April 2, Las Vegas, Nevada. Use code FABINSIDER for $400 discount. Register now
- Microsoft Fabric Community
- Fabric community blogs
- Power BI Community Blog
- R script as data source in Power BI Desktop
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Purpose of this blog post is to demonstrate how to use R script to load and prepare data source in Power BI desktop. R is open source powerful statistical analysis and visualisation language. Integrating R in Power BI lets you undertake complex data manipulation tasks. In this post I am going to use two sample csv dataset that contains raw data for import and export amounts for various Australian territories, and using R transform it to right format to be visualised in Power BI desktop. I am only going to cover basics of R to get data into the shape required so that you can use more interesting functions of R in future.
Prerequisites
For this post I am assuming you have basic understanding of R and its concepts such as data frame, packages (though we will not require any special package to be installed for this tutorial) and its syntax. Almost everything that you can think of can be done with functions in R and for this tutorial we are only going to work with base R functions.
Setup
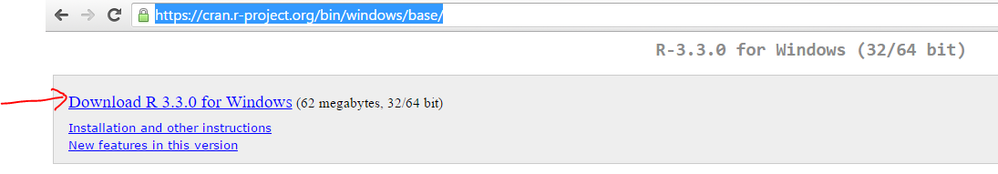
Download and install latest version of R for windows from https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/base/.
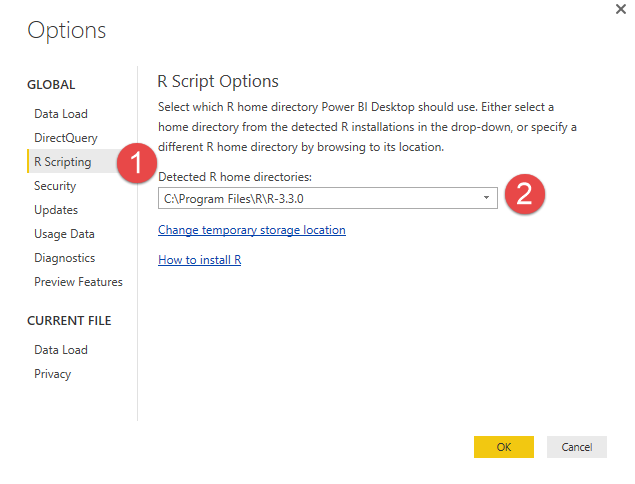
Once R is installed in powerbi desktop ensure R data source is pointed to the correct location. If you have selected default location during R installation no change is required however if you’ve used custom location then you need to point R data source in powerbi desktop accordingly. To update that in powerbi desktop go to File > Options and Settings > Options > R Scripting > Detected R home directories > Other and browse to the location where R is installed.
Import
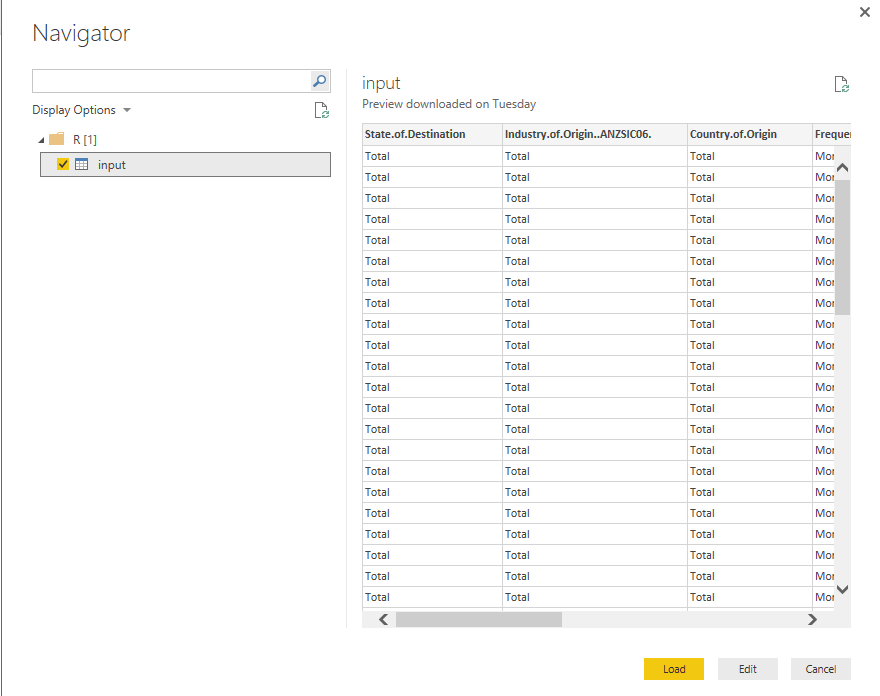
To import data into powerbi using R, go to Get Data > Other > R Script > Connect which will give you dialog box to enter in R scripts. Files I've used for this post is attached below.
Copy and paste below code that will import contents of csv file into a table called input and see in preview navigator. Using ‘~//’ will look for csv file in the default folder of R installation which is in Documents folder however you can specify custom path using double backslashes for example C:\\Users\\abc\\Desktop\\AU_Import.csv. It is also good practise to explicitly mention separator and you can use comma or tab delimiter as required.
#use read.csv method to import data
input <- read.csv("~//AU_Import.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
Formatting & Sorting
Majority of times not all the data available is useful and you may only need the small subset of data from the actual file. Here we are only interested in columns Frequency, Commodity, Time and Value. Also changing column names to more meaningful ones.
#use read.csv method to import data
input <- read.csv("~//AU_Import.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Destination","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
input <- input[,keepcolumns]
colnames(input)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(input)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(input)[5] <- c("ImportValue")
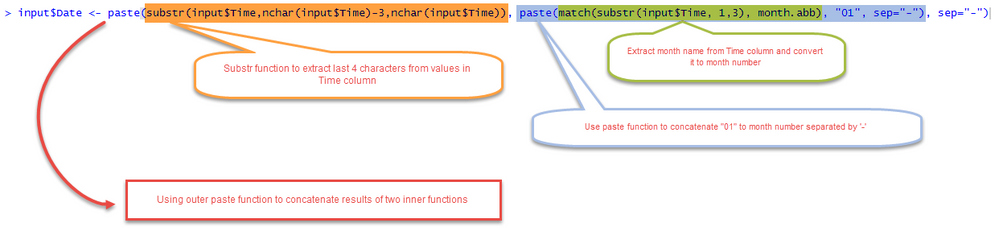
If you notice Time column has values in 'mmm-yyyy’ format which will be recognized as characters by R and text based field in power bi and therefore won’t allow time based slicing and dicing. To convert values into proper date format we will make use of several R functions. Using Paste, Substr functions to extract month name out of values in Time column, convert it to month number, append ‘01’ to it and paste that to last 5 characters of Time column resulting in Date column in ‘dd-mm-yyyy’ format. Time column is then not required and can be removed.
#use read.csv method to import data
input <- read.csv("~//AU_Import.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Destination","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
input <- input[,keepcolumns]
colnames(input)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(input)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(input)[5] <- c("ImportValue")
#extract monthname
input$Date <- paste(substr(input$Time,nchar(input$Time)-3,nchar(input$Time)), paste(match(substr(input$Time, 1,3), month.abb), "01", sep="-"), sep="-")
#Time column no longer required
attach(input)
input$Time <- NULL
We will then use Date column to sort using Order function. By default sorting is ascending.
#use read.csv method to import data
input <- read.csv("~//AU_Import.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Destination","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
input <- input[,keepcolumns]
colnames(input)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(input)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(input)[5] <- c("ImportValue")
#extract monthname
input$Date <- paste(substr(input$Time,nchar(input$Time)-3,nchar(input$Time)), paste(match(substr(input$Time, 1,3), month.abb), "01", sep="-"), sep="-")
#Time column no longer required
attach(input)
input$Time <- NULL
#change data type of Date column to date
input$Date <- as.Date(input$Date)
#sort by date column
input[order(Date),]
Filtering
As we’re only interested in state level data, using subset function we can filter out rows that is not useful. Using ‘!=’ operator and ‘&’ operator to specify multiple conditions we are going to excluded rows where there is no state details, commodity totals and state totals. Using Omit function will remove all rows where value is null.
#use read.csv method to import data
input <- read.csv("~//AU_Import.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Destination","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
input <- input[,keepcolumns]
colnames(input)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(input)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(input)[5] <- c("ImportValue")
#extract monthname
input$Date <- paste(substr(input$Time,nchar(input$Time)-3,nchar(input$Time)), paste(match(substr(input$Time, 1,3), month.abb), "01", sep="-"), sep="-")
#Time column no longer required
attach(input)
input$Time <- NULL
#change data type of Date column to date
input$Date <- as.Date(input$Date)
#sort by date column
input[order(Date),]
#Use subset function to exclude rows
input <- subset(input, Commodity!="TOTAL" & State!="No state details" & State!="Total")
#Use omit function to remove null rows
input <- na.omit(input)
Similarly we will prepare export data into a data frame called output using above code.
#use read.csv method to import data
output <- read.csv("~//AU_Export.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Origin","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
output <- output[,keepcolumns]
colnames(output)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(output)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(output)[5] <- c("ExportValue")
#extract monthname
output$Date <- paste(substr(output$Time,nchar(output$Time)-3,nchar(output$Time)), paste(match(substr(output$Time, 1,3), month.abb), "01", sep="-"), sep="-")
#Time column no longer required
attach(output)
output$Time <- NULL
#change data type of Date column to date
output$Date <- as.Date(output$Date)
#sort by date column
output[order(Date),]
#Use subset function to exclude rows
output <- subset(output, Commodity!="TOTAL" & State!="No state details" & State!="Total")
#Use omit function to remove null rows
output <- na.omit(output)
Merging
Finally we want to merge these two data frames into single one to be used in power bi. We will use merge function for that and specify columns we want to perform match on.
#use read.csv method to import data
input <- read.csv("~//AU_Import.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Destination","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
input <- input[,keepcolumns]
colnames(input)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(input)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(input)[5] <- c("ImportValue")
#extract monthname
input$Date <- paste(substr(input$Time,nchar(input$Time)-3,nchar(input$Time)), paste(match(substr(input$Time, 1,3), month.abb), "01", sep="-"), sep="-")
#Time column no longer required
attach(input)
input$Time <- NULL
#change data type of Date column to date
input$Date <- as.Date(input$Date)
#sort by date column
input[order(Date),]
#Use subset function to exclude rows
input <- subset(input, Commodity!="TOTAL" & State!="No state details" & State!="Total")
#Use omit function to remove null rows
input <- na.omit(input)
#use read.csv method to import Export data
output <- read.csv("~//AU_Export.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Origin","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
output <- output[,keepcolumns]
colnames(output)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(output)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(output)[5] <- c("ExportValue")
#extract monthname
output$Date <- paste(substr(output$Time,nchar(output$Time)-3,nchar(output$Time)), paste(match(substr(output$Time, 1,3), month.abb), "01", sep="-"), sep="-")
#Time column no longer required
attach(output)
output$Time <- NULL
#change data type of Date column to date
output$Date <- as.Date(output$Date)
#sort by date column
output[order(Date),]
#Use subset function to exclude rows
output <- subset(output, Commodity!="TOTAL" & State!="No state details" & State!="Total")
#Use omit function to remove null rows
output <- na.omit(output)
#Use merge function to merge two dataframes
Combined <- merge(input,output,by=c("State","Frequency","Commodity","Date"))
Transforming
To calculate percentage values for each row in Import and Export columns, using basic arithmetic operation we will divide each value by sum of values in that column and then format it to display with percentage sign using Paste function.
#use read.csv method to import data
input <- read.csv("~//AU_Import.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Destination","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
input <- input[,keepcolumns]
colnames(input)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(input)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(input)[5] <- c("ImportValue")
#extract monthname
input$Date <- paste(substr(input$Time,nchar(input$Time)-3,nchar(input$Time)), paste(match(substr(input$Time, 1,3), month.abb), "01", sep="-"), sep="-")
#Time column no longer required
attach(input)
input$Time <- NULL
#change data type of Date column to date
input$Date <- as.Date(input$Date)
#sort by date column
input[order(Date),]
#Use subset function to exclude rows
input <- subset(input, Commodity!="TOTAL" & State!="No state details" & State!="Total")
#Use omit function to remove null rows
input <- na.omit(input)
#use read.csv method to import Export data
output <- read.csv("~//AU_Export.csv", stringsAsFactors=FALSE, sep=",")
#excluding unwanted columns and change column names
keepcolumns <- c("State.of.Origin","Frequency","Commodity.by.SITC","Time","Value")
output <- output[,keepcolumns]
colnames(output)[3] <- c("Commodity")
colnames(output)[1] <- c("State")
colnames(output)[5] <- c("ExportValue")
#extract monthname
output$Date <- paste(substr(output$Time,nchar(output$Time)-3,nchar(output$Time)), paste(match(substr(output$Time, 1,3), month.abb), "01", sep="-"), sep="-")
#Time column no longer required
attach(output)
output$Time <- NULL
#change data type of Date column to date
output$Date <- as.Date(output$Date)
#sort by date column
output[order(Date),]
#Use subset function to exclude rows
output <- subset(output, Commodity!="TOTAL" & State!="No state details" & State!="Total")
#Use omit function to remove null rows
output <- na.omit(output)
#Use merge function to merge two datasets
Combined <- merge(input,output,by=c("State","Frequency","Commodity","Date"))
#New columns calculating percentage values for each Import and Export
Combined$ImportValuePct <- Combined$ImportValue / sum(Combined$ImportValue)
Combined$ExportValuePct <- Combined$ExportValue / sum(Combined$ExportValue)
#Format columns to show values in percentage
Combined$ImportValuePct <- paste(round(Combined$ImportValuePct*100,digits=1),"%",sep="")
Combined$ExportValuePct <- paste(round(Combined$ExportValuePct*100,digits=1),"%",sep="")
As a result of above code three tables will be created in power bi however we will only be interested in table Combined which is the outcome of above transformations.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
- Understanding TMDL in Power BI: A Game-Changer for...
- 🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 1 F...
- 🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 1 W...
- 🏆 Power BI DataViz Campeonato mundial! Semana 1!
- Fabric Capacity Scaling and Power BI - What happen...
- 🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | ¡La sema...
- 🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 2 C...
- How to Use Multi-Cursor in Power BI TMDL View
- 🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Meet the...
- Securing Data using Sensitivity Labels in Power BI
-
 Pragati11
on:
🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 1 W...
Pragati11
on:
🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 1 W...
-
 slindsay
on:
🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 2 C...
slindsay
on:
🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 2 C...
-
 slindsay
on:
🏆 Power BI Data Visualization World Championships...
slindsay
on:
🏆 Power BI Data Visualization World Championships...
-
 slindsay
on:
🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 1 C...
slindsay
on:
🏆 Power BI DataViz World Championships | Week 1 C...
- Jalə on: Developing an Azerbaijan Shape Map
- ccarawan_1 on: Frequently Asked Questions | Power BI DataViz Worl...
- LYPowerBI on: Using Variables While Creating Custom Columns in P...
- cravity-hub on: Embedding Power BI Report in Web Pages
-
Poweraegg
 on:
Connecting Fact Tables in Microsoft Fabric: A Brid...
on:
Connecting Fact Tables in Microsoft Fabric: A Brid...
-
 PradipVS
on:
Power BI - Powered by Copilot
PradipVS
on:
Power BI - Powered by Copilot
-
How to
647 -
Tips & Tricks
616 -
Support insights
121 -
Events
121 -
Opinion
80 -
DAX
66 -
Power BI
65 -
Power Query
62 -
Power BI Dev Camp
45 -
Power BI Desktop
40 -
Roundup
37 -
Power BI Embedded
20 -
Time Intelligence
19 -
Tips&Tricks
18 -
Featured User Group Leader
15 -
PowerBI REST API
12 -
Dataflow
9 -
Power BI Service
8 -
Power Query Tips & Tricks
8 -
finance
8 -
Data Protection
7 -
Direct Query
7 -
Data Visualization
6 -
Python
6 -
Power BI REST API
6 -
Auto ML
6 -
financial reporting
6 -
Data Analysis
6 -
Power Automate
6 -
Power BI PowerShell
5 -
Machine Learning
5 -
Income Statement
5 -
Dax studio
5 -
powerbi
5 -
service
5 -
PowerShell
4 -
Desktop
4 -
Bookmarks
4 -
Line chart
4 -
Group By
4 -
community
4 -
RLS
4 -
M language
4 -
Paginated Reports
4 -
External tool
4 -
Power BI Goals
4 -
Reports
3 -
PowerApps
3 -
Data Science
3 -
Azure
3 -
Data model
3 -
Conditional Formatting
3 -
Visualisation
3 -
Administration
3 -
M code
3 -
Visuals
3 -
SQL Server 2017 Express Edition
3 -
R script
3 -
Aggregation
3 -
calendar
3 -
Gateways
3 -
R
3 -
M Query
3 -
Webinar
3 -
CALCULATE
3 -
R visual
3 -
PBI Desktop
2 -
Date Dimension
2 -
Integer
2 -
Visualization
2 -
Power BI Challenge
2 -
Query Parameter
2 -
Date
2 -
SharePoint
2 -
Power BI Installation and Updates
2 -
How Things Work
2 -
Tabular Editor
2 -
rank
2 -
ladataweb
2 -
Troubleshooting
2 -
Date DIFF
2 -
Transform data
2 -
Tips and Tricks
2 -
Incremental Refresh
2 -
Number Ranges
2 -
Query Plans
2 -
Power BI & Power Apps
2 -
Random numbers
2 -
Day of the Week
2 -
Custom Visual
2 -
VLOOKUP
2 -
pivot
2 -
calculated column
2 -
M
2 -
hierarchies
2 -
Power BI Anniversary
2 -
Language M
2 -
inexact
2 -
Date Comparison
2 -
Power BI Premium Per user
2 -
Forecasting
2 -
REST API
2 -
Editor
2 -
Split
2 -
Life Sciences
2 -
measure
2 -
Microsoft-flow
2 -
Paginated Report Builder
2 -
Working with Non Standatd Periods
2 -
powerbi.tips
2 -
Custom function
2 -
Reverse
2 -
PUG
2 -
Custom Measures
2 -
Filtering
2 -
Row and column conversion
2 -
Python script
2 -
Nulls
2 -
DVW Analytics
2 -
parameter
2 -
Industrial App Store
2 -
Week
2 -
Date duration
2 -
Formatting
2 -
Weekday Calendar
2 -
Support insights.
2 -
construct list
2 -
slicers
2 -
SAP
2 -
Power Platform
2 -
Workday
2 -
external tools
2 -
index
2 -
RANKX
2 -
Workspace
1 -
Theme Colours
1 -
Text
1 -
Flow
1 -
Publish to Web
1 -
Extract
1 -
Topper Color On Map
1 -
Historians
1 -
context transition
1 -
Custom textbox
1 -
OPC
1 -
Zabbix
1 -
Label: DAX
1 -
Business Analysis
1 -
Supporting Insight
1 -
rank value
1 -
Synapse
1 -
End of Week
1 -
Tips&Trick
1 -
Showcase
1 -
custom connector
1 -
Waterfall Chart
1 -
Power BI On-Premise Data Gateway
1 -
patch
1 -
Top Category Color
1 -
A&E data
1 -
Previous Order
1 -
Substring
1 -
Wonderware
1 -
Power M
1 -
Format DAX
1 -
Custom functions
1 -
accumulative
1 -
DAX&Power Query
1 -
Premium Per User
1 -
GENERATESERIES
1 -
Report Server
1 -
Audit Logs
1 -
analytics pane
1 -
step by step
1 -
Top Brand Color on Map
1 -
Tutorial
1 -
Previous Date
1 -
XMLA End point
1 -
color reference
1 -
Date Time
1 -
Marker
1 -
Lineage
1 -
CSV file
1 -
conditional accumulative
1 -
Matrix Subtotal
1 -
Check
1 -
null value
1 -
Excel
1 -
Cumulative Totals
1 -
Report Theme
1 -
Bookmarking
1 -
oracle
1 -
mahak
1 -
pandas
1 -
Networkdays
1 -
Button
1 -
Dataset list
1 -
Keyboard Shortcuts
1 -
Fill Function
1 -
LOOKUPVALUE()
1 -
Tips &Tricks
1 -
Plotly package
1 -
Healthcare
1 -
Sameperiodlastyear
1 -
Office Theme
1 -
matrix
1 -
bar chart
1 -
Measures
1 -
powerbi argentina
1 -
Canvas Apps
1 -
total
1 -
Filter context
1 -
Difference between two dates
1 -
get data
1 -
OSI
1 -
Query format convert
1 -
ETL
1 -
Json files
1 -
Merge Rows
1 -
CONCATENATEX()
1 -
take over Datasets;
1 -
Networkdays.Intl
1 -
refresh M language Python script Support Insights
1 -
Governance
1 -
Fun
1 -
Power BI gateway
1 -
gateway
1 -
Elementary
1 -
Custom filters
1 -
Vertipaq Analyzer
1 -
powerbi cordoba
1 -
Model Driven Apps
1 -
REMOVEFILTERS
1 -
XMLA endpoint
1 -
translations
1 -
OSI pi
1 -
Parquet
1 -
Change rows to columns
1 -
remove spaces
1 -
Get row and column totals
1 -
Retail
1 -
Power BI Report Server
1 -
School
1 -
Cost-Benefit Analysis
1 -
DIisconnected Tables
1 -
Sandbox
1 -
Honeywell
1 -
Combine queries
1 -
X axis at different granularity
1 -
ADLS
1 -
Primary Key
1 -
Microsoft 365 usage analytics data
1 -
Randomly filter
1 -
Week of the Day
1 -
Azure AAD
1 -
query
1 -
Dynamic Visuals
1 -
KPI
1 -
Intro
1 -
Icons
1 -
ISV
1 -
Ties
1 -
unpivot
1 -
Practice Model
1 -
Continuous streak
1 -
ProcessVue
1 -
Create function
1 -
Table.Schema
1 -
Acknowledging
1 -
Postman
1 -
Text.ContainsAny
1 -
Power BI Show
1 -
Get latest sign-in data for each user
1 -
API
1 -
Kingsley
1 -
Merge
1 -
variable
1 -
Issues
1 -
function
1 -
stacked column chart
1 -
ho
1 -
ABB
1 -
KNN algorithm
1 -
List.Zip
1 -
optimization
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Map Visual
1 -
Text.ContainsAll
1 -
Tuesday
1 -
help
1 -
group
1 -
Scorecard
1 -
Json
1 -
Tops
1 -
financial reporting hierarchies RLS
1 -
Featured Data Stories
1 -
MQTT
1 -
Custom Periods
1 -
Partial group
1 -
Reduce Size
1 -
FBL3N
1 -
Wednesday
1 -
Power Pivot
1 -
Quick Tips
1 -
data
1 -
PBIRS
1 -
Usage Metrics in Power BI
1 -
Multivalued column
1 -
Pipeline
1 -
Path
1 -
Yokogawa
1 -
Dynamic calculation
1 -
Data Wrangling
1 -
native folded query
1 -
transform table
1 -
UX
1 -
Cell content
1 -
General Ledger
1 -
Thursday
1 -
Table
1 -
Natural Query Language
1 -
Infographic
1 -
automation
1 -
Prediction
1 -
newworkspacepowerbi
1 -
Performance KPIs
1 -
HR Analytics
1 -
keepfilters
1 -
Connect Data
1 -
Financial Year
1 -
Schneider
1 -
dynamically delete records
1 -
Copy Measures
1 -
Friday
1 -
Q&A
1 -
Event
1 -
Custom Visuals
1 -
Free vs Pro
1 -
Format
1 -
Active Employee
1 -
Custom Date Range on Date Slicer
1 -
refresh error
1 -
PAS
1 -
certain duration
1 -
DA-100
1 -
bulk renaming of columns
1 -
Single Date Picker
1 -
Monday
1 -
PCS
1 -
Saturday
1 -
update
1 -
Slicer
1 -
Visual
1 -
forecast
1 -
Regression
1 -
CICD
1 -
Current Employees
1 -
date hierarchy
1 -
relationship
1 -
SIEMENS
1 -
Multiple Currency
1 -
Power BI Premium
1 -
On-premises data gateway
1 -
Binary
1 -
Power BI Connector for SAP
1 -
Sunday
1 -
Training
1 -
Announcement
1 -
Features
1 -
domain
1 -
pbiviz
1 -
sport statistics
1 -
Intelligent Plant
1 -
Circular dependency
1 -
GE
1 -
Exchange rate
1 -
Dendrogram
1 -
range of values
1 -
activity log
1 -
Decimal
1 -
Charticulator Challenge
1 -
Field parameters
1 -
deployment
1 -
ssrs traffic light indicators
1 -
SQL
1 -
trick
1 -
Scripts
1 -
Color Map
1 -
Industrial
1 -
Weekday
1 -
Working Date
1 -
Space Issue
1 -
Emerson
1 -
Date Table
1 -
Cluster Analysis
1 -
Stacked Area Chart
1 -
union tables
1 -
Number
1 -
Start of Week
1 -
Tips& Tricks
1