FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now! Learn more
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Summarizing values
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Summarizing values
Hi I saw this question in one website.
You have a Power BI report named Orders that supports the following analysis:
✑ Total sales over time
✑ The count of orders over time
✑ New and repeat customer counts
The data model size is nearing the limit for a dataset in shared capacity.
The model view for the dataset is shown in the following exhibit.
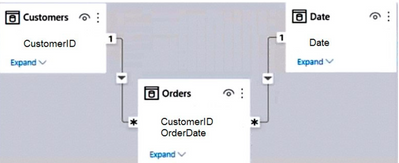
Answer :

Why is the answer No for the first option?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @KV2022 ,
Is your problem solved? If so, would you mind accept the helpful replies as solutions? Then we are able to close the thread. More people who have the same requirment will find the solution quickly and benefit here, thank you!
Best Regards,
Community Support Team _ kalyj
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@KV2022 ,
By summarizing the data into a single table, what you would end up with is an extra table that stores and duplicates data from your fact and dimensions. This typically would be called denormalized tables. The question indicates that your shared capacity is nearing its limit for a dataset size so adding "bloat" to your model is not recommended.
In addition, we typically like to "normalize" the model by splitting factual data, considering keys and aggregations, in one table, and attributes in dimension tables to reduce data duplication / redundancy.
Did I answer your question?
Please help by clicking the thumbs up button and mark my post as a solution!
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now!

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 40 | |
| 36 | |
| 33 | |
| 29 | |
| 26 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 134 | |
| 104 | |
| 63 | |
| 60 | |
| 55 |

