FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Vote for your favorite vizzies from the Power BI Dataviz World Championship submissions. Vote now!
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Re: Moving Average
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
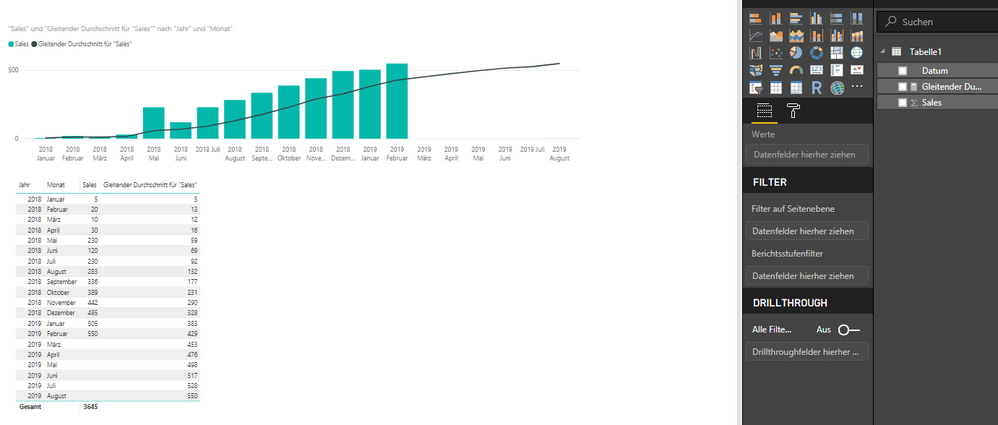
Moving Average
Hey,
I tried to go for the Moving Average building with PowerBI.
The problem is that the moving average is calculated for the future, which does not make any sense.
I wanted to do a six-month-rolling average with the quick measure (problem of above appeared), then with the formula = calculate(average([Sales]), DatesInPeriod([date];Lastdate([date]), -6, MONTH). Same Problem, again. So I do not know what is the problem. Perhaps somebody could offer me a simple sample PBIX data with a 6 month moving average over 2 years data..
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Rotergnom2,
I would suggest you create a date table in your scenario. Please check out the attached demo and the measure below.
Measure =
VAR maxFactDate =
CALCULATE ( MAX ( FactTable[Date] ), ALL ( 'Calendar' ) )
RETURN
IF (
MAX ( 'Calendar'[Date] ) > maxFactDate,
BLANK (),
CALCULATE (
AVERAGEX (
SUMMARIZE (
'FactTable',
'Calendar'[Date].[Year],
'Calendar'[Date].[Month],
"MonthTotal", SUM ( FactTable[Sales] )
),
[MonthTotal]
),
DATESINPERIOD ( 'Calendar'[date], LASTDATE ( 'Calendar'[date] ), -6, MONTH )
)
)
Best Regards,
Dale
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Rotergnom2,
Could you please mark the proper answer as a solution?
Best Regards,
Dale
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Rotergnom2,
I would suggest you create a date table in your scenario. Please check out the attached demo and the measure below.
Measure =
VAR maxFactDate =
CALCULATE ( MAX ( FactTable[Date] ), ALL ( 'Calendar' ) )
RETURN
IF (
MAX ( 'Calendar'[Date] ) > maxFactDate,
BLANK (),
CALCULATE (
AVERAGEX (
SUMMARIZE (
'FactTable',
'Calendar'[Date].[Year],
'Calendar'[Date].[Month],
"MonthTotal", SUM ( FactTable[Sales] )
),
[MonthTotal]
),
DATESINPERIOD ( 'Calendar'[date], LASTDATE ( 'Calendar'[date] ), -6, MONTH )
)
)
Best Regards,
Dale
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
So, is your calculation correct other than the fact that it includes future estimations?
Follow on LinkedIn
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: DAX For Humans
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
Vote for your favorite vizzies from the Power BI World Championship submissions!

Join our Community Sticker Challenge 2026
If you love stickers, then you will definitely want to check out our Community Sticker Challenge!

Power BI Monthly Update - January 2026
Check out the January 2026 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 63 | |
| 51 | |
| 41 | |
| 23 | |
| 18 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 134 | |
| 111 | |
| 50 | |
| 31 | |
| 29 |