FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now! Learn more
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Re: How to Show Contiguous Sum Trend Based on Time...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
How to Show Contiguous Sum Trend Based on Timestamped Value Table
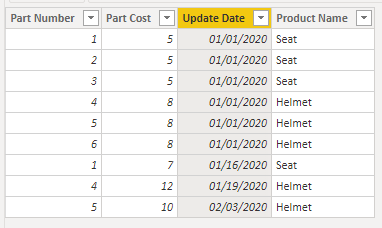
I am being provided a dataset from Cost Accounting that has the list of all costed Parts and the time that part was costed (and a "Product" is generally made of multiple costed "Parts"). When a Part's cost is changed, a new row is created with the updated cost and is timestamped with the date the cost was changed. The dataset looks like this:
Part Number | Part Cost | Update Date | Product Name
001 5 1-Jan-20 Seat
002 5 1-Jan-20 Seat
003 5 1-Jan-20 Seat
004 8 1-Jan-20 Helmet
005 8 1-Jan-20 Helmet
006 8 1-Jan-20 Helmet
001 7 16-Jan-20 Seat
004 12 19-Jan-20 Helmet
005 10 3-Feb-20 Helmet
The real dataset is roughly 70k unique parts with up to 30 changes each over a 10 year period.
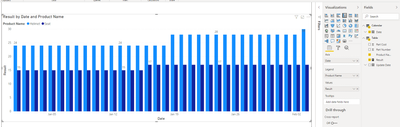
My end goal is to have a measure that can show the Product's cost on a line chart with a contiguous date axis. When filtered to "Seat" the chart would show a cost of $15 up through 16JAN, where the cost would then update to $17, and so on. When filtered on "Helmet", it would show a cost of $24 up through 19JAN where it would then show $28, then update to $30 on 03FEB and show that through present day.
Thank you in advance for any advice! I've been stumped and searching hasn't turned up anything useful.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, @Anonymous
Based on your description, I created data to reproduce your scenario. The pbix file is attached in the end.
Table:
Calendar(a calculated table):
Calendar = CALENDARAUTO()
There is no relationship between two tables. You may create a measure as below.
Result =
var tab =
ADDCOLUMNS(
SUMMARIZE(
FILTER(
ALL('Table'),
'Table'[Update Date]<=SELECTEDVALUE('Calendar'[Date])
),
'Table'[Product Name],
'Table'[Part Number],
"MaxDate",MAX('Table'[Update Date])
),
"Cost",
CALCULATE(
SUM('Table'[Part Cost]),
FILTER(
ALL('Table'),
'Table'[Product Name]=EARLIER('Table'[Product Name])&&
'Table'[Part Number]=EARLIER('Table'[Part Number])&&
'Table'[Update Date]=EARLIER([MaxDate])
)
)
)
return
SUMX(
FILTER(
tab,
[Product Name]=SELECTEDVALUE('Table'[Product Name])
),
[Cost]
)
Result:
Best Regards
Allan
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, @Anonymous
Based on your description, I created data to reproduce your scenario. The pbix file is attached in the end.
Table:
Calendar(a calculated table):
Calendar = CALENDARAUTO()
There is no relationship between two tables. You may create a measure as below.
Result =
var tab =
ADDCOLUMNS(
SUMMARIZE(
FILTER(
ALL('Table'),
'Table'[Update Date]<=SELECTEDVALUE('Calendar'[Date])
),
'Table'[Product Name],
'Table'[Part Number],
"MaxDate",MAX('Table'[Update Date])
),
"Cost",
CALCULATE(
SUM('Table'[Part Cost]),
FILTER(
ALL('Table'),
'Table'[Product Name]=EARLIER('Table'[Product Name])&&
'Table'[Part Number]=EARLIER('Table'[Part Number])&&
'Table'[Update Date]=EARLIER([MaxDate])
)
)
)
return
SUMX(
FILTER(
tab,
[Product Name]=SELECTEDVALUE('Table'[Product Name])
),
[Cost]
)
Result:
Best Regards
Allan
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
Helpful resources

Power BI Monthly Update - November 2025
Check out the November 2025 Power BI update to learn about new features.

Fabric Data Days
Advance your Data & AI career with 50 days of live learning, contests, hands-on challenges, study groups & certifications and more!

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 58 | |
| 45 | |
| 41 | |
| 20 | |
| 18 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 172 | |
| 110 | |
| 91 | |
| 55 | |
| 45 |