Fabric Data Days starts November 4th!
Advance your Data & AI career with 50 days of live learning, dataviz contests, hands-on challenges, study groups & certifications and more!
Get registeredGet Fabric Certified for FREE during Fabric Data Days. Don't miss your chance! Request now
- Microsoft Fabric Community
- Fabric community blogs
- Power BI Community Blog
- How to put the row and column subtotals in front o...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Scenario:
Although there is no direct operation to put the total row in front of the matrix column in Power bi, we can still make it by using below two methods.
1. Use the summarized function to form a new table of data string “Total”, and add a space string at the top of it, then add the new table to the original one through the union function, and finally, “Total with spaces” will go to the top automatically when they match alphabetically.
2. Create a special column that contains “Total” and " Total" contains empty characters. According to the alphabetical order, it will be the first column in the matrix. Create a measure to determine whether the selected is " Total", Yes, SUM is performed, if not, the current value is assigned.
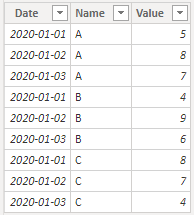
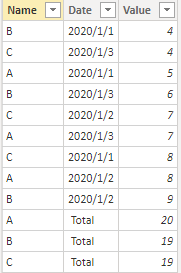
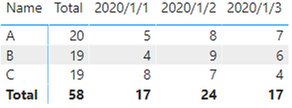
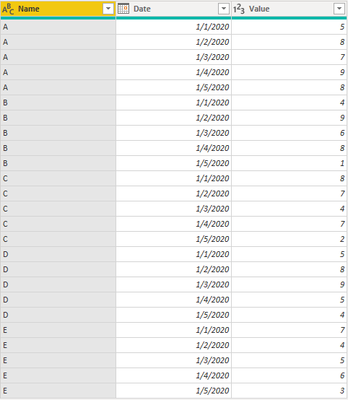
Sample Data:
‘Row Table’: Here's the sample table that contains the data between 2020 / 1 / 1 and 2020 / 1 / 3 to calculate the row subtotal.
‘Column Table’: Here's the sample table that contains the data between 2020 / 1 / 1 and 2020 / 1 / 3 to calculate the column subtotal.
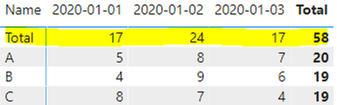
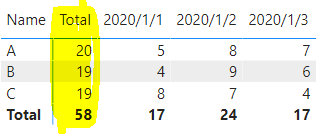
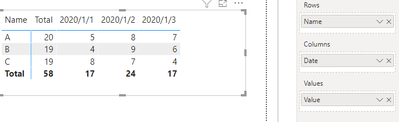
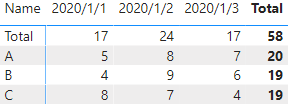
Expected output:
‘Row Table’:
‘Column Table’:
Guideline:
There are two methods:
- Method 1:
Row Subtotal:
- Create a table of calculations grouped by Date add two columns named Name and Value, where ‘Name’ is the “Total’ string with spaces and value is that in the original ‘row Table” to be added as per the Date group.
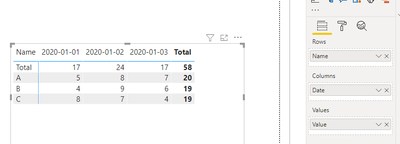
- As far as we can see, I added three rows to the end of the original data table and used the name column as " Total", created a matrix and placed it, rows = ‘Row Table’[name], column = ‘Row Table’[name], values = ‘Row Table’[Value].
Column Subtotal:
- Create a table of calculations grouped by name, add two columns named Date and Value, where ‘Date’ is the “Total’ string with spaces and value is that in the original ‘column Table” to be added as per the name group.
- As far as we can see, I added three rows to the end of the original data table and used the name column as " Total", created a matrix and placed it, rows = ‘Column Table’[name], column = ‘Column Table’[name], values = ‘Column Table’[Value].
- Method 2:
Row Subtotal:
- Use distinct to de-duplicate the data of 'Row Table'[Name] to form a Table1, and use the datatable() function to form a Name column. The data is Table2 with a space string " Total", and finally, use Union to append the two tables to form a separate table ‘Name select’, and create the relationship between the table ‘Name select’ and the table ‘Row Table’.
- Put the data in the table into the matrix in this form (Row= 'Column Table'[Name], Column= 'Date select’[Date], Values= 'Column Table'[Value]), then you will see “Total” in the matrix, since the string with a space is sorted alphabetically, it will be sorted to the left automatically. Then we created a measure to determine whether the selection is " Total", Yes, SUM will be performed, if not, the current value will be assigned.
Column Subtotal:
- Use distinct to de-duplicate the data of 'Column Table'[Date] to form a Table1, and use the datatable() function to form a date column. The data is Table2 with a space string" Total", and finally, use Union to append the two tables to form a separate table ‘Date select’, and create the relationship between the table ‘Date select’ and the table ‘Column Table’.
2. Put the data in the table into the matrix in this form (Row= 'Column Table'[Name], Column= ‘Date select’[Date], Values= ‘Column Table’[Value]), then you will see “Total” in the matrix, since the string with a space is sorted alphabetically, it will be sorted to the left automatically. Then we create a measure to determine whether the selection is " Total", Yes, SUM will be performed, if not, the current value will be assigned.
Operations:
- Method 1:
Row Subtotal:
- Create a calculated table to group by Date, add two columns named Name and Value, Name is the string" Total" with spaces, and Value is the value in the original table ‘Row Table’ to be added according to the Date group.
‘Row SubTotal’ =
VAR _summarize =
SUMMARIZE (
'‘Row Table’',
[Date],
"Name", " Total",
"Value", SUM ( ’Row Table’[Value] )
)
RETURN
UNION ( '‘Row Table’', _summarize )
Note:
The space character in " Total" will automatically rank Total according to the alphabetical order to the leftmost side of the matrix to prevent confusion due to the alphabetical order.
Result:
Step analysis:
Use the summarize function to create a calculated table with the Date column as the group, the Name column as the “Total”, and the Value column data as the added calculated column table after grouping, and then use the union function to append the calculated table and ‘Row Table’.
- As far as we can see, I added three rows to the end of the original data table and used the name column as " Total", creating a matrix and placing it, rows = ‘Row Table’[name], column = ‘Row Table’[name], values = ‘Row Table’[Value].
Result:
Step analysis:
The Name column of the new formed table “Row Sub Total” is composed of ABC type data and " Total". After placing it in the matrix, " Total" will be placed on the leftmost side according to the alphabetical order due to the space string.
Column Subtotal
- Create a table of calculations grouped by name, add two columns named Date and Value, where ‘Date’ is the “Total’ string with spaces and value is that in the original ‘column Table” to be added as per the name group.
‘Column Sub Total’ =
VAR _summarize =
SUMMARIZE (
'‘Column Table’',
[Name],
"Date", " Total",
"Value", SUM ( ’Column Table’[Value] )
)
RETURN
UNION ( '‘Column Table’', _summarize )
Result:
Step analysis:
Use the summarize function to create a calculated table with the Name column as the grouping and the Date column as " Total", and the Value column data as the added calculated column table after grouping, and then use the union function to append the calculated table and ‘Column Table’.
- As far as we can see, I added three rows to the end of the original data table and used the name column as " Total", created a matrix and placed it, rows = ‘Column Table’[name], column = ‘Column Table’[name], values = ‘Column Table’[Value].
Result:
Step analysis:
The Date column of the new table ‘Column Sub Total’ formed is composed of 2020/1/1 date type data and " Total". After placing it in the matrix, " Total" will be placed on the leftmost side according to the alphabetical order due to the space string.
- Method 2:
Row Subtotal:
- Use distinct to de-duplicate the data of ‘Row Table’[Name] to form a Table1, and use the datatable() function to form a Name column. The data is Table2 with a space string " Total", and finally, use Union to append the two tables to form a separate table ‘Name select’, and create the relationship between the table ‘Name select’ and the table ‘Row Table’.
‘Name select’ =
UNION (
DISTINCT ( ’Row Table’[Name] ),
DATATABLE ( "Name", STRING, { { " Total" } } )
)
Result:
Step analysis:
Use distinct to de-duplicate the name in the table ‘Row Table’, use datatable() to create data containing " Total" in the Name column, and perform union to form ABC type data and " Total" table ‘Name select’.
- Put the data in the table into the matrix in this form (Row= 'Column Table'[Name], Column= 'Date select’[Date], Values= 'Column Table'[Value]), then you will see “Total” in the matrix, since the string with a space is sorted alphabetically, it will be sorted to the left automatically. Then we created a measure to determine whether the selection is " Total", Yes, SUM will be performed, if not, the current value will be assigned.
Row Subtotal second =
IF (
SELECTEDVALUE ( '‘Name select’'[Name] ) = " Total",
CALCULATE ( SUM ( ’Row Table’[Value] ), ALL ( '‘Name select’'[Name] ) ),
SUM ( ’Row Table’[Value] )
)
Result:
Step analysis:
When ‘Name select’ '[Name] Selected data " Total" when the value of the Value will be summed according to Date, otherwise, it returns the current value of.
Column Subtotal:
- Use distinct to de-duplicate the data of ‘Column Table’[Date] to form a Table1, and use the datatable() function to form a date column. The data is Table2 with a space string " Total", and finally, use Union to append the two tables to form a separate table ‘Date select’, and create the relationship between the table ‘Date select’ and the table.
‘Date select’ =
UNION (
DISTINCT ( ’Column Table’[Date] ),
DATATABLE ( "Date", STRING, { { " Total" } } )
)
Result:
Step analysis:
Use distinct to de-duplicate the name in the table ‘Column Table’, use datatable() to create data containing " Total" in the date column, and perform union to form 2020/1/1 date type data and" Total" table ‘Date select’.
- Put the data in the table into the matrix in this form (Row= 'Column Table'[Name], Column= ‘Date select’[Date], Values= ‘Column Table’[Value]), then you will see “Total” in the matrix, since the string with a space is sorted alphabetically, it will be sorted to the left automatically. Then we created a measure to determine whether the selection is " Total", Yes, SUM will be performed, if not, the current value will be assigned.
Column Subtotal second =
IF (
SELECTEDVALUE ( ’Date select’'[Date] ) = " Total",
CALCULATE ( SUM ( ’Column Table’[Value] ), ALL ( ’Date select’'[Date] ) ),
SUM ( ’Column Table’[Value] )
)
Result:
Step analysis:
When ‘Date select’'[Date] Selected data " Total" when the value of the Value will be summed according to name, otherwise, it returns the current value of.
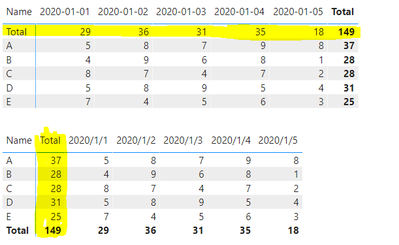
Output:
This is the expected table chart.
The blank character before the " Total" makes it the first column in the Matrix because the columns in the Matrix of Power BI are sorted in ascending order from the first character.
We can verify if the results are correct by adding the data.
Add the following data to the two original tables:
Row Subtotal:
Column Subtotal:
The results of the matrix are as follows:
The result is the same as I expected.
Please refer to the attachment below for details.
I hope this article can help you with the similar question.
Author: Yang Liu
Reviewer: Ula Huang, Kerry Wang
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
- QuickViz Challenge | Raise the Bar!
- Power Query Functions Explained: From Simple Clean...
- Understanding DAX Time Intelligence with Additiona...
- QuickViz Challenges | Fabric Data Days
- Notebooks Contest | Fabric Data Days
- Dataviz Contest for Pros | Fabric Data Days
- Fabric Data Days | Join a Study Group
- Student Dataviz Contest | Fabric Data Days
- Understanding Power BI Relationships & Filter Dire...
- Power BI usage analysis via Measure Killer, by Man...
-
sazidthe1
 on:
QuickViz Challenge | Raise the Bar!
on:
QuickViz Challenge | Raise the Bar!
-
Magudeswaran_MR
 on:
Understanding DAX Time Intelligence with Additiona...
on:
Understanding DAX Time Intelligence with Additiona...
-
 slindsay
on:
QuickViz Challenges | Fabric Data Days
slindsay
on:
QuickViz Challenges | Fabric Data Days
-
sazidthe1
 on:
Notebooks Contest | Fabric Data Days
on:
Notebooks Contest | Fabric Data Days
- Sourav9144 on: Dataviz Contest for Pros | Fabric Data Days
- Anjor on: Fabric Data Days | Join a Study Group
-
Magudeswaran_MR
 on:
Understanding Power BI Relationships & Filter Dire...
on:
Understanding Power BI Relationships & Filter Dire...
- Vikranth426 on: Are they Drill Down and Drill Through both are Sam...
-
 FabricPam
on:
Fabric Data Days | Full Schedule
FabricPam
on:
Fabric Data Days | Full Schedule
- PawelJasz on: Interactive DAX Exercises Trainer – Track Progress...
-
How to
732 -
Tips & Tricks
710 -
Events
174 -
Support insights
121 -
Opinion
88 -
DAX
66 -
Power BI
65 -
Power Query
62 -
Power BI Dev Camp
45 -
Power BI Desktop
40 -
Roundup
38 -
Dataflow
30 -
Featured User Group Leader
26 -
Power BI Embedded
20 -
Time Intelligence
19 -
Tips&Tricks
18 -
Data Protection
15 -
PowerBI REST API
12 -
Power Query Tips & Tricks
8 -
finance
8 -
Power BI Service
8 -
Direct Query
7 -
Power BI REST API
6 -
Auto ML
6 -
financial reporting
6 -
Data Analysis
6 -
Power Automate
6 -
Data Visualization
6 -
Python
6 -
Tips and Tricks
6 -
Income Statement
5 -
Dax studio
5 -
powerbi
5 -
service
5 -
Power BI PowerShell
5 -
Machine Learning
5 -
RLS
4 -
M language
4 -
Life Sciences
4 -
Paginated Reports
4 -
External tool
4 -
Power BI Goals
4 -
Desktop
4 -
PowerShell
4 -
Bookmarks
4 -
Line chart
4 -
Group By
4 -
community
4 -
Data model
3 -
Conditional Formatting
3 -
Visualisation
3 -
Administration
3 -
M code
3 -
Visuals
3 -
SQL Server 2017 Express Edition
3 -
R script
3 -
Aggregation
3 -
Webinar
3 -
calendar
3 -
Gateways
3 -
R
3 -
M Query
3 -
CALCULATE
3 -
R visual
3 -
Reports
3 -
PowerApps
3 -
Data Science
3 -
Azure
3 -
Custom Visual
2 -
VLOOKUP
2 -
pivot
2 -
calculated column
2 -
M
2 -
hierarchies
2 -
Power BI Anniversary
2 -
Language M
2 -
inexact
2 -
Date Comparison
2 -
Power BI Premium Per user
2 -
Forecasting
2 -
REST API
2 -
Editor
2 -
Split
2 -
measure
2 -
Microsoft-flow
2 -
Paginated Report Builder
2 -
Working with Non Standatd Periods
2 -
powerbi.tips
2 -
Custom function
2 -
Reverse
2 -
PUG
2 -
Custom Measures
2 -
Filtering
2 -
Row and column conversion
2 -
Python script
2 -
Nulls
2 -
DVW Analytics
2 -
parameter
2 -
Industrial App Store
2 -
Week
2 -
Date duration
2 -
Formatting
2 -
Weekday Calendar
2 -
Support insights.
2 -
construct list
2 -
slicers
2 -
SAP
2 -
Power Platform
2 -
Workday
2 -
external tools
2 -
index
2 -
RANKX
2 -
Date
2 -
PBI Desktop
2 -
Date Dimension
2 -
Integer
2 -
Visualization
2 -
Power BI Challenge
2 -
Query Parameter
2 -
SharePoint
2 -
Power BI Installation and Updates
2 -
How Things Work
2 -
Tabular Editor
2 -
rank
2 -
ladataweb
2 -
Troubleshooting
2 -
Date DIFF
2 -
Transform data
2 -
Healthcare
2 -
Incremental Refresh
2 -
Number Ranges
2 -
Query Plans
2 -
Power BI & Power Apps
2 -
Random numbers
2 -
Day of the Week
2 -
Retail
1 -
Power BI Report Server
1 -
School
1 -
Cost-Benefit Analysis
1 -
DIisconnected Tables
1 -
Sandbox
1 -
Honeywell
1 -
Combine queries
1 -
X axis at different granularity
1 -
ADLS
1 -
Primary Key
1 -
Microsoft 365 usage analytics data
1 -
Randomly filter
1 -
Week of the Day
1 -
Azure AAD
1 -
query
1 -
Dynamic Visuals
1 -
KPI
1 -
Intro
1 -
Icons
1 -
ISV
1 -
Ties
1 -
unpivot
1 -
Practice Model
1 -
Continuous streak
1 -
ProcessVue
1 -
Create function
1 -
Table.Schema
1 -
Acknowledging
1 -
Postman
1 -
Text.ContainsAny
1 -
Power BI Show
1 -
Get latest sign-in data for each user
1 -
Power Pivot
1 -
API
1 -
Kingsley
1 -
Merge
1 -
variable
1 -
Issues
1 -
function
1 -
stacked column chart
1 -
ho
1 -
ABB
1 -
KNN algorithm
1 -
List.Zip
1 -
optimization
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Map Visual
1 -
Text.ContainsAll
1 -
Tuesday
1 -
help
1 -
group
1 -
Scorecard
1 -
Json
1 -
Tops
1 -
financial reporting hierarchies RLS
1 -
Featured Data Stories
1 -
MQTT
1 -
Custom Periods
1 -
Partial group
1 -
Reduce Size
1 -
FBL3N
1 -
Wednesday
1 -
Q&A
1 -
Quick Tips
1 -
data
1 -
PBIRS
1 -
Usage Metrics in Power BI
1 -
Multivalued column
1 -
Pipeline
1 -
Path
1 -
Yokogawa
1 -
Dynamic calculation
1 -
Data Wrangling
1 -
native folded query
1 -
transform table
1 -
UX
1 -
Cell content
1 -
General Ledger
1 -
Thursday
1 -
update
1 -
Table
1 -
Natural Query Language
1 -
Infographic
1 -
automation
1 -
Prediction
1 -
newworkspacepowerbi
1 -
Performance KPIs
1 -
HR Analytics
1 -
keepfilters
1 -
Connect Data
1 -
Financial Year
1 -
Schneider
1 -
dynamically delete records
1 -
Copy Measures
1 -
Friday
1 -
Training
1 -
Event
1 -
Custom Visuals
1 -
Free vs Pro
1 -
Format
1 -
Active Employee
1 -
Custom Date Range on Date Slicer
1 -
refresh error
1 -
PAS
1 -
certain duration
1 -
DA-100
1 -
bulk renaming of columns
1 -
Single Date Picker
1 -
Monday
1 -
PCS
1 -
Saturday
1 -
Slicer
1 -
Visual
1 -
forecast
1 -
Regression
1 -
CICD
1 -
Current Employees
1 -
date hierarchy
1 -
relationship
1 -
SIEMENS
1 -
Multiple Currency
1 -
Power BI Premium
1 -
On-premises data gateway
1 -
Binary
1 -
Power BI Connector for SAP
1 -
Sunday
1 -
Workspace
1 -
Announcement
1 -
Features
1 -
domain
1 -
pbiviz
1 -
sport statistics
1 -
Intelligent Plant
1 -
Circular dependency
1 -
GE
1 -
Exchange rate
1 -
Dendrogram
1 -
range of values
1 -
activity log
1 -
Decimal
1 -
Charticulator Challenge
1 -
Field parameters
1 -
deployment
1 -
ssrs traffic light indicators
1 -
SQL
1 -
trick
1 -
Scripts
1 -
Color Map
1 -
Industrial
1 -
Weekday
1 -
Working Date
1 -
Space Issue
1 -
Emerson
1 -
Date Table
1 -
Cluster Analysis
1 -
Stacked Area Chart
1 -
union tables
1 -
Number
1 -
Start of Week
1 -
Tips& Tricks
1 -
Theme Colours
1 -
Text
1 -
Flow
1 -
Publish to Web
1 -
Extract
1 -
Topper Color On Map
1 -
Historians
1 -
context transition
1 -
Custom textbox
1 -
OPC
1 -
Zabbix
1 -
Label: DAX
1 -
Business Analysis
1 -
Supporting Insight
1 -
rank value
1 -
Synapse
1 -
End of Week
1 -
Tips&Trick
1 -
Excel
1 -
Showcase
1 -
custom connector
1 -
Waterfall Chart
1 -
Power BI On-Premise Data Gateway
1 -
patch
1 -
Top Category Color
1 -
A&E data
1 -
Previous Order
1 -
Substring
1 -
Wonderware
1 -
Power M
1 -
Format DAX
1 -
Custom functions
1 -
accumulative
1 -
DAX&Power Query
1 -
Premium Per User
1 -
GENERATESERIES
1 -
Report Server
1 -
Audit Logs
1 -
analytics pane
1 -
step by step
1 -
Top Brand Color on Map
1 -
Tutorial
1 -
Previous Date
1 -
XMLA End point
1 -
color reference
1 -
Date Time
1 -
Marker
1 -
Lineage
1 -
CSV file
1 -
conditional accumulative
1 -
Matrix Subtotal
1 -
Check
1 -
null value
1 -
Show and Tell
1 -
Cumulative Totals
1 -
Report Theme
1 -
Bookmarking
1 -
oracle
1 -
mahak
1 -
pandas
1 -
Networkdays
1 -
Button
1 -
Dataset list
1 -
Keyboard Shortcuts
1 -
Fill Function
1 -
LOOKUPVALUE()
1 -
Tips &Tricks
1 -
Plotly package
1 -
Sameperiodlastyear
1 -
Office Theme
1 -
matrix
1 -
bar chart
1 -
Measures
1 -
powerbi argentina
1 -
Canvas Apps
1 -
total
1 -
Filter context
1 -
Difference between two dates
1 -
get data
1 -
OSI
1 -
Query format convert
1 -
ETL
1 -
Json files
1 -
Merge Rows
1 -
CONCATENATEX()
1 -
take over Datasets;
1 -
Networkdays.Intl
1 -
refresh M language Python script Support Insights
1 -
Tutorial Requests
1 -
Governance
1 -
Fun
1 -
Power BI gateway
1 -
gateway
1 -
Elementary
1 -
Custom filters
1 -
Vertipaq Analyzer
1 -
powerbi cordoba
1 -
Model Driven Apps
1 -
REMOVEFILTERS
1 -
XMLA endpoint
1 -
translations
1 -
OSI pi
1 -
Parquet
1 -
Change rows to columns
1 -
remove spaces
1 -
Get row and column totals
1
- 11-02-2025 - 11-08-2025
- 10-26-2025 - 11-01-2025
- 10-19-2025 - 10-25-2025
- 10-12-2025 - 10-18-2025
- 10-05-2025 - 10-11-2025
- 09-28-2025 - 10-04-2025
- 09-21-2025 - 09-27-2025
- 09-14-2025 - 09-20-2025
- 09-07-2025 - 09-13-2025
- 08-31-2025 - 09-06-2025
- 08-24-2025 - 08-30-2025
- 08-17-2025 - 08-23-2025
- 08-10-2025 - 08-16-2025
- View Complete Archives