Fabric Data Days starts November 4th!
Advance your Data & AI career with 50 days of live learning, dataviz contests, hands-on challenges, study groups & certifications and more!
Get registered- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Get Fabric Certified for FREE during Fabric Data Days. Don't miss your chance! Learn more
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Re: Power Query text parsing and splitting into re...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Power Query text parsing and splitting into records
Hi,
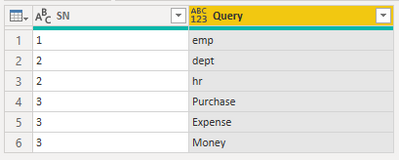
I have the following scenario - data looks like this as exmaple below :
| ID | Query |
| 1 | select * from emp |
| 2 | select * from dept UNION select * from hr |
| 3 | select * from Purchase JOIN Expense ON Purchase. key = Expense.key JOIN Money ON Expense.key1 = Money.key1 |
required outcome:
| ID | Table |
| 1 | emp |
| 2 | dept |
| 2 | hr |
| 3 | Purchase |
| 3 | Expense |
| 3 | Money |
tried with Text.BetweenDelimiters and Table.SplitColumn , but not able to get this.
Please help.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
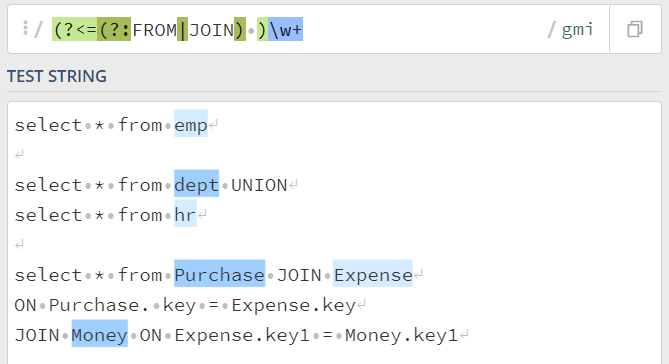
let
Source = Table.FromRows(Json.Document(Binary.Decompress(Binary.FromText("i45WMlTSUSpOzUlNLlHQUkgrys9VSM0tUIrViVYywpBJSS0oUQj18/T3i8lDlckoAmsxxtASUFqUnJFYnKrg5e/pp+BaUZAK1BmT5+8Hl9FTyE6tVLCFyekBeTF5YNW++XlAGX8/ZClDoEqwOJijFBsLAA==", BinaryEncoding.Base64), Compression.Deflate)), let _t = ((type nullable text) meta [Serialized.Text = true]) in type table [SN = _t, Query = _t]),
#"Extracted table" = Table.TransformColumns(Source, {"Query", each let l = List.Select(Text.SplitAny(_, " #(lf)"), each _<>""), pos = List.PositionOfAny(l, {"FROM", "JOIN"}, Occurrence.All, Comparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase) in List.Accumulate(pos, {}, (s,c) => s&{l{c+1}})}),
#"Expanded Query" = Table.ExpandListColumn(#"Extracted table", "Query")
in
#"Expanded Query"| Thanks to the great efforts by MS engineers to simplify syntax of DAX! Most beginners are SUCCESSFULLY MISLED to think that they could easily master DAX; but it turns out that the intricacy of the most frequently used RANKX() is still way beyond their comprehension! |
DAX is simple, but NOT EASY! |
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Resort to embedded R or Python with regular expression,
| Thanks to the great efforts by MS engineers to simplify syntax of DAX! Most beginners are SUCCESSFULLY MISLED to think that they could easily master DAX; but it turns out that the intricacy of the most frequently used RANKX() is still way beyond their comprehension! |
DAX is simple, but NOT EASY! |
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
let
Source = Table.FromRows(Json.Document(Binary.Decompress(Binary.FromText("i45WMlTSUSpOzUlNLlHQUkgrys9VSM0tUIrViVYywpBJSS0oUQj18/T3i8lDlckoAmsxxtASUFqUnJFYnKrg5e/pp+BaUZAK1BmT5+8Hl9FTyE6tVLCFyekBeTF5YNW++XlAGX8/ZClDoEqwOJijFBsLAA==", BinaryEncoding.Base64), Compression.Deflate)), let _t = ((type nullable text) meta [Serialized.Text = true]) in type table [SN = _t, Query = _t]),
#"Extracted table" = Table.TransformColumns(Source, {"Query", each let l = List.Select(Text.SplitAny(_, " #(lf)"), each _<>""), pos = List.PositionOfAny(l, {"FROM", "JOIN"}, Occurrence.All, Comparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase) in List.Accumulate(pos, {}, (s,c) => s&{l{c+1}})}),
#"Expanded Query" = Table.ExpandListColumn(#"Extracted table", "Query")
in
#"Expanded Query"| Thanks to the great efforts by MS engineers to simplify syntax of DAX! Most beginners are SUCCESSFULLY MISLED to think that they could easily master DAX; but it turns out that the intricacy of the most frequently used RANKX() is still way beyond their comprehension! |
DAX is simple, but NOT EASY! |
Helpful resources

Fabric Data Days
Advance your Data & AI career with 50 days of live learning, contests, hands-on challenges, study groups & certifications and more!

Power BI Monthly Update - October 2025
Check out the October 2025 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 80 | |
| 49 | |
| 35 | |
| 31 | |
| 30 |