Fabric Data Days starts November 4th!
Advance your Data & AI career with 50 days of live learning, dataviz contests, hands-on challenges, study groups & certifications and more!
Get registered- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Get Fabric Certified for FREE during Fabric Data Days. Don't miss your chance! Request now
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- How to add zero values for missing sales months so...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
How to add zero values for missing sales months so the data is evenly spaced for forecasting?
I am trying to do forecasting in Power BI for a very large number of parts. For parts having demand in every month, the forecasting runs perfectly. For parts which does not have demand in some months, the forecast will either show up without considering the months or else the error will pop up saying the data is irregular to forecast. I know I have to add zero values for those parts for the missing months. The question is how to add zero values for such large number of parts so that the forecast shows up and is accurate?
The parts are around 50000 and the demand is monthly demand for 36 months. Also, the data editing needs to be minimal on Excel because this needs to be a real time based dashboard.
Does anyone know how to solve this problem?
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @meetrachhadia9,
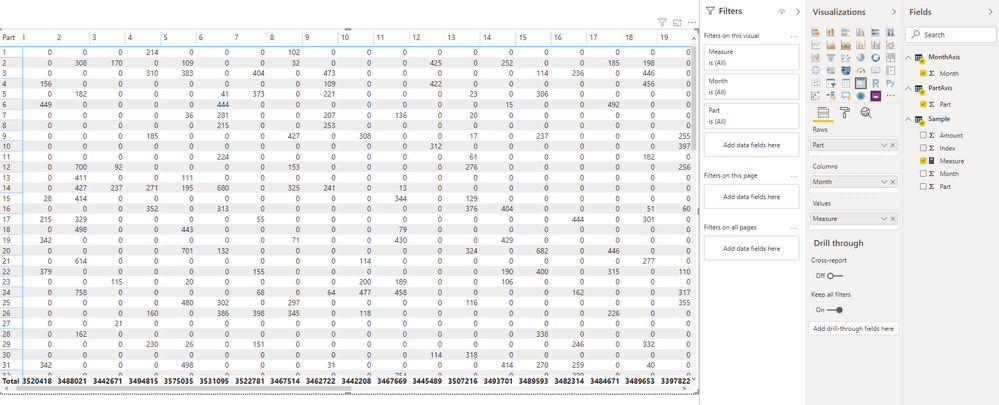
Did your table contain all month and parts? If this is a case, you can create new tables to extract and store 'parts' and 'month' values.
Then you can create matrix visual with new tables fields as axis and write a measure to lookup value from the original table based on current part and month. (matrix design: month to column, part to row, measure to value)
Calculate tables:
MonthAxis = VALUES('Sample'[Month])
PartAxis = VALUES('Sample'[Part])
Measure:
Measure =
VAR currMonth =
VALUES ( MonthAxis[Month] )
VAR currPart =
VALUES ( PartAxis[Part] )
RETURN
CALCULATE (
SUM ( 'Sample'[Amount] ),
FILTER ( ALLSELECTED ( 'Sample' ), [Month] IN currMonth && [Part] IN currPart )
) + 0
If your source table only contains less amount of records that can't extract full category fields value.
You need to prepare two tables with full category values(part, month), then you can use them with measure formula to generate an expanded matrix visual with correspond result.
BTW, if you only want a new table with full records mapping, you can try to use cross join function to achieve your requirement:
Table =
ADDCOLUMNS (
CROSSJOIN ( VALUES ( 'Sample'[Part] ), VALUES ( 'Sample'[Month] ) ),
"Amount", CALCULATE (
SUM ( 'Sample'[Amount] ),
FILTER (
ALLSELECTED ( 'Sample' ),
[Month] = EARLIER ( 'Sample'[Month] )
&& [Part] = EARLIER ( 'Sample'[Part] )
)
) + 0
)
Regards,
Xiaoxin Sheng
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @meetrachhadia9,
Did your table contain all month and parts? If this is a case, you can create new tables to extract and store 'parts' and 'month' values.
Then you can create matrix visual with new tables fields as axis and write a measure to lookup value from the original table based on current part and month. (matrix design: month to column, part to row, measure to value)
Calculate tables:
MonthAxis = VALUES('Sample'[Month])
PartAxis = VALUES('Sample'[Part])
Measure:
Measure =
VAR currMonth =
VALUES ( MonthAxis[Month] )
VAR currPart =
VALUES ( PartAxis[Part] )
RETURN
CALCULATE (
SUM ( 'Sample'[Amount] ),
FILTER ( ALLSELECTED ( 'Sample' ), [Month] IN currMonth && [Part] IN currPart )
) + 0
If your source table only contains less amount of records that can't extract full category fields value.
You need to prepare two tables with full category values(part, month), then you can use them with measure formula to generate an expanded matrix visual with correspond result.
BTW, if you only want a new table with full records mapping, you can try to use cross join function to achieve your requirement:
Table =
ADDCOLUMNS (
CROSSJOIN ( VALUES ( 'Sample'[Part] ), VALUES ( 'Sample'[Month] ) ),
"Amount", CALCULATE (
SUM ( 'Sample'[Amount] ),
FILTER (
ALLSELECTED ( 'Sample' ),
[Month] = EARLIER ( 'Sample'[Month] )
&& [Part] = EARLIER ( 'Sample'[Part] )
)
) + 0
)
Regards,
Xiaoxin Sheng
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Tough to say, are you using a measure? Please see this post regarding How to Get Your Question Answered Quickly: https://community.powerbi.com/t5/Community-Blog/How-to-Get-Your-Question-Answered-Quickly/ba-p/38490
Follow on LinkedIn
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: DAX For Humans
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
Helpful resources

Fabric Data Days
Advance your Data & AI career with 50 days of live learning, contests, hands-on challenges, study groups & certifications and more!

Power BI Monthly Update - October 2025
Check out the October 2025 Power BI update to learn about new features.