Become a Certified Power BI Data Analyst!
Join us for an expert-led overview of the tools and concepts you'll need to pass exam PL-300. The first session starts on June 11th. See you there!
Get registered- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Power BI is turning 10! Let’s celebrate together with dataviz contests, interactive sessions, and giveaways. Register now.
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Average of 3 Months
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Average of 3 Months
Hi
I need Average of the SUM of the Total of a Month and previous 2 Months so it will be 3 Months Average in front of each Month.
As there are multiple transactions in a month so the logic I am looking for is to SUM(Total) for each Month and then Evaluate Average for Current Month and Previous 2.
for e.g.
Jan shows Average of Jan
Feb shows Average of Jan-Feb
Mar shows Average of Jan-Feb-Mar
Apr shows Average of Feb-Mar-Apr
Data is here,
| OrderDate | Year | Month | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total |
| 1/6/16 | 2016 | Jan | East | Jones | Pencil | 0 | ||
| 1/23/16 | 2016 | Jan | Central | Kivell | Binder | 50 | 19.99 | 999.5 |
| 2/9/16 | 2016 | Feb | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 |
| 2/26/16 | 2016 | Feb | Central | Gill | Pen | 27 | 19.99 | 539.73 |
| 3/15/16 | 2016 | Mar | West | Sorvino | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 |
| 4/1/16 | 2016 | Apr | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 4.99 | 299.4 |
| 4/18/16 | 2016 | Apr | Central | Andrews | Pencil | 75 | 1.99 | 149.25 |
| 5/5/16 | 2016 | May | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 90 | 4.99 | 449.1 |
| 5/22/16 | 2016 | May | West | Thompson | Pencil | 32 | 1.99 | 63.68 |
| 6/8/16 | 2016 | Jun | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 8.99 | 539.4 |
| 6/25/16 | 2016 | Jun | Central | Morgan | Pencil | 90 | 4.99 | 449.1 |
| 7/12/16 | 2016 | Jul | East | Howard | Binder | 29 | 1.99 | 57.71 |
| 7/29/16 | 2016 | Jul | East | Parent | Binder | 81 | 19.99 | 1619.19 |
| 8/15/16 | 2016 | Aug | East | Jones | Pencil | 35 | 4.99 | 174.65 |
| 9/1/16 | 2016 | Sep | Central | Smith | Desk | 0 | ||
| 9/18/16 | 2016 | Sep | East | Jones | Pen Set | 16 | 15.99 | 255.84 |
| 10/5/16 | 2016 | Oct | Central | Morgan | Binder | 28 | 8.99 | 251.72 |
| 10/22/16 | 2016 | Oct | East | Jones | Pen | 64 | 8.99 | 575.36 |
| 11/8/16 | 2016 | Nov | East | Parent | Pen | 15 | 19.99 | 299.85 |
| 11/25/16 | 2016 | Nov | Central | Kivell | Pen Set | 0 | ||
| 12/12/16 | 2016 | Dec | Central | Smith | Pencil | 67 | 1.29 | 86.43 |
| 12/29/16 | 2016 | Dec | East | Parent | Pen Set | 74 | 15.99 | 1183.26 |
| 1/15/17 | 2017 | Jan | Central | Gill | Binder | 46 | 8.99 | 413.54 |
| 2/1/17 | 2017 | Feb | Central | Smith | Binder | 87 | 15 | 1305 |
| 2/18/17 | 2017 | Feb | East | Jones | Binder | 0 | ||
| 3/7/17 | 2017 | Mar | West | Sorvino | Binder | 0 | ||
| 3/24/17 | 2017 | Mar | Central | Jardine | Pen Set | 50 | 4.99 | 249.5 |
| 4/10/17 | 2017 | Apr | Central | Andrews | Pencil | 66 | 1.99 | 131.34 |
| 4/27/17 | 2017 | Apr | East | Howard | Pen | 0 | ||
| 5/14/17 | 2017 | May | Central | Gill | Pencil | 53 | 1.29 | 68.37 |
| 5/31/17 | 2017 | May | Central | Gill | Binder | 80 | 8.99 | 719.2 |
| 6/17/17 | 2017 | Jun | Central | Kivell | Desk | 0 | ||
| 7/4/17 | 2017 | Jul | East | Jones | Pen Set | 62 | 4.99 | 309.38 |
| 7/21/17 | 2017 | Jul | Central | Morgan | Pen Set | 55 | 12.49 | 686.95 |
| 8/7/17 | 2017 | Aug | Central | Kivell | Pen Set | 42 | 23.95 | 1005.9 |
| 8/24/17 | 2017 | Aug | West | Sorvino | Desk | 0 | ||
| 9/10/17 | 2017 | Sep | Central | Gill | Pencil | 0 | ||
| 9/27/17 | 2017 | Sep | West | Sorvino | Pen | 76 | 1.99 | 151.24 |
| 10/14/17 | 2017 | Oct | West | Thompson | Binder | 57 | 19.99 | 1139.43 |
| 10/31/17 | 2017 | Oct | Central | Andrews | Pencil | 14 | 1.29 | 18.06 |
| 11/17/17 | 2017 | Nov | Central | Jardine | Binder | 11 | 4.99 | 54.89 |
| 12/4/17 | 2017 | Dec | Central | Jardine | Binder | 0 | ||
| 12/21/17 | 2017 | Dec | Central | Andrews | Binder | 28 | 4.99 | 139.72 |
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @iamprajot
You should set up your data model with a Date table containing a YearMonth column of some sort, related to your "Sales" table (I'll assume that's the name).
Something like this: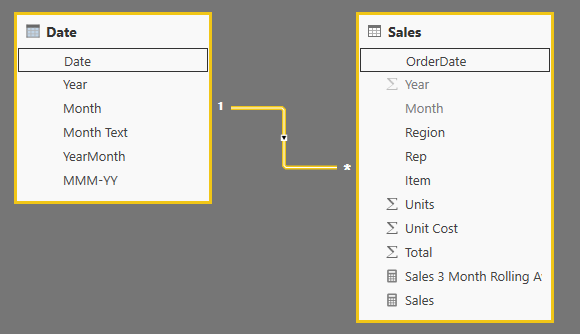
Then you can define measures like this:
Sales = SUM ( Sales[Total] )
Sales 3 Month Rolling Average =
CALCULATE (
AVERAGEX ( VALUES ( 'Date'[YearMonth] ), [Sales] ),
DATESINPERIOD ( 'Date'[Date], MAX ( 'Date'[Date] ), -3, MONTH )
)
The AVERAGEX function will automatically exclude months that either don't exist or have BLANK sales, so that in Jan-16 only one month will be averaged for example.
Regards,
Owen
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @iamprajot
You should set up your data model with a Date table containing a YearMonth column of some sort, related to your "Sales" table (I'll assume that's the name).
Something like this:
Then you can define measures like this:
Sales = SUM ( Sales[Total] )
Sales 3 Month Rolling Average =
CALCULATE (
AVERAGEX ( VALUES ( 'Date'[YearMonth] ), [Sales] ),
DATESINPERIOD ( 'Date'[Date], MAX ( 'Date'[Date] ), -3, MONTH )
)
The AVERAGEX function will automatically exclude months that either don't exist or have BLANK sales, so that in Jan-16 only one month will be averaged for example.
Regards,
Owen
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, i have tried the formula used above and also tried this formula pasted, but i keep getting the cumulative of what im calculating and not the average,is there something wrong with my dax?
3 month avg = CALCULATE(AVERAGEX(Dim_Brokerage;Dim_Brokerage[Brokerage]);DATESINPERIOD(Dim_Date[Date];LASTDATE(Dim_Date[Date]);-3;MONTH))
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks but I have already tried this and few other ways but my problem is different, no matter if you "create a separate Date Table and create relation" or "Create a Date Calculated Column", this will not solve the problem.
Let me explain the difference what I found, I can get Sum of Total for every Month in Pivot Table and then Add 3 Months and divide it with 3
but in Power BI, I can get Sum of Total for every Month BUT when it comes to Average, Power BI does not add 3 months, instead it adds 2-3 transactions of a month and divide it with number of transactions OR add Jan-Feb-Mar but DO NOT DIVIDE IT WITH 3 instead divided it with number of transactions in Jan-Feb-Mar, which is 6.
What I am thinking is to use SUMMARIZE function to create a Table with Dates and Sum of Total and use that table inside ADDCOLUMNS in which I could use the DATESINPERIOD.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi again @iamprajot
The expression I used above within the measure AVERAGEX ( VALUES ( 'Date'[YearMonth] ), [Sales] ) should do what you want.
Using AVERAGEX this way, [Sales] is calculated for each YearMonth value (in the context of the measure it is at most 3 values), and these are then averaged with equal weighting.
Here is a sample pbix that illustrates the calculation.
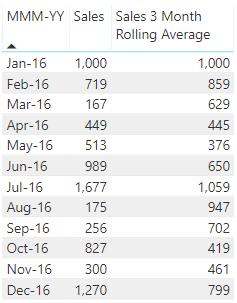
An excerpt from a table in that file looks like this.
- Jan-16 rolling avg = (1,000)/1 = 1,000
- Feb-16 rolling avg = (1,000 + 719)/2 = 859
- Mar-16 rolling avg = (1,000 + 719 + 167)/3 = 629
I think that's what you want. Can you get something similar working in your model?
Regards,
Owen
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Sorry and yeah it's working but in order for it to work a separate date table is mandatory.
I was neglecting the Calendar Table and tried creating those date columns within the Data Table so that's why it was not working.
Also I got another help and found the below which is the same thing except there is no need to create the Calendar Table.
MAT =
CALCULATE (
AVERAGEX (
SUMMARIZE (
Data,
Data[OrderDate].[Year],
Data[OrderDate].[Month],
"MAT", SUM ( Data[Total] )
),
[MAT]
),
DATESINPERIOD (
Data[OrderDate].[Date],
LASTDATE ( Data[OrderDate].[Date] ),
-3,
MONTH
)
)
Thanks so much for help, now I am clear about both concepts.
Helpful resources

Join our Fabric User Panel
This is your chance to engage directly with the engineering team behind Fabric and Power BI. Share your experiences and shape the future.

Power BI Monthly Update - June 2025
Check out the June 2025 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 78 | |
| 76 | |
| 53 | |
| 37 | |
| 31 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 101 | |
| 56 | |
| 51 | |
| 45 | |
| 40 |