FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Vote for your favorite vizzies from the Power BI Dataviz World Championship submissions. Vote now!
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Re: Add rows / missing date values
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Add rows / missing date values
Hi all.
Recently I found out that my dataset from SQL server lacks some information. My dataset is about machine units and their daily performance. However, if a unit did not work some particular day (maintenance or whatever), the entry with corresponding date is not stored. For example, a CAT unit didn't work on Jan 4th and I would like it to be stored as zero. Here is the example of my database and a modified one.
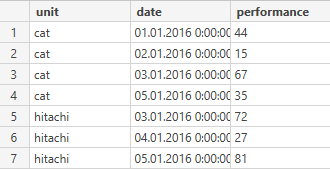
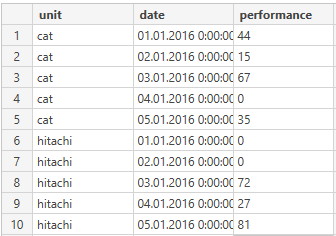
What is the best way to make this modifications?
The initial problem is that the average monthly performance is calculated wrong (it divides total performance by only table-existing days in january, not all 31 days). Make monthly performance in a separate table could make sense, but then I guess it will lack of time intelligence, drill downs, and there are more indicators, not only performance. But if you think it is a better idea, let me know.
I really appreciate any help.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @karimkz.
In your scenario, you can follow below steps to achieve your requirement:
1. Duplicate this query connect to the SQL Server database, filter the original query only keep cat data, rename it as cat table. Also filter the duplicated table to only keep hitachi data, rename it as hitachi table.
2. Create a calendar table.
3. Merge the calendar table with cat table and hitachi table separately. For the unit column, use Fill down or up, for the value column, use Replaces values as 0.
4. Append the cat table with hitachi table.
For more information, please check attached .pbix file.
Best Regards,
Qiuyun Yu
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thank you for your answer!
I see your point, I believe it will work out. Gotta learn how to do all that things though.
Also I think of creating a date table, then do something like:
CALCULATE(SUM(performance); FILTER(date; date.month=EARLIEST(month))).
Do you think it will work?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi
we also have the same situation , but our tables are very huge so cant make it duplicate , is ithere any way for this issue , did you got the solution
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Creating a calendar table and merging it with the existing table is still a best option.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
You need to dimensionalise your data. I would create a separte date table and a seperate unit table (with the distinct list of unit types). You can then use a calculations like this:
CALCULATE
(
AVERAGEX
(
CROSSJOIN
(
VALUES('Unit'[Unit]),
VALUES('Date'[Date])
)
,SUM([Performance])
)
)
CROSSJOIN will give you the product of all dates and all units that are currently being filtered. Then AVERAGEX will iterate over this calculating the SUM and then finally calculating the average.
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
Vote for your favorite vizzies from the Power BI World Championship submissions!

Join our Community Sticker Challenge 2026
If you love stickers, then you will definitely want to check out our Community Sticker Challenge!

Power BI Monthly Update - January 2026
Check out the January 2026 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 58 | |
| 53 | |
| 43 | |
| 17 | |
| 16 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 123 | |
| 108 | |
| 44 | |
| 32 | |
| 24 |
