FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Learn from the best! Meet the four finalists headed to the FINALS of the Power BI Dataviz World Championships! Register now
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Power Query
- Very Slow Performance on Group By
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Very Slow Performance on Group By
Hi,
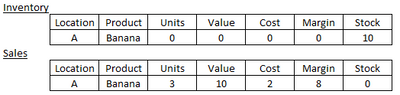
Unfortunately, our inventory and sales data reside in different systems so I have had to construct two data queries to bring this information in to Power Query. I have constructed the two queries so that in they are laid out in the same format:
I've then appended the two queries and performed a group by on the Location and Product, aggregating the measure fields. However, the volume of data is such that it's taken nearly an hour so far to load the data into the Power BI data model, with no sign that is near to being finished. In total I have approx 13.5m rows of inventory data and 2.5m rows of sales data. Below is the actual M code being generated by Power Query. Is there anything I can do to make this more efficient? I thought the append rather than a merge with full outer join would be a more efficient way of doing this, but so far it's not proving that way!
let
#"Sales Query" = SapHana.Database("xxxxxxxx:xxxxx", [Query="select#(tab)CREATION_WEEK as WEEK_ID,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)ltrim(gsv.PRCTR, '0') as SITE,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)GENERIC,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)sum(UNITS) as UNITS,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)sum(NET_VALUE) as NET_VALUE,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)sum(NDW) as COST_OF_SALES,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)sum(GROSS_MARGIN) as GROSS_MARGIN,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)0 as STOCK#(lf)#(lf)from aggregates.global_single_view gsv#(lf)#(lf)left join ""_SYS_BIC"".""EuropeMerch/CV_MER_LOCATION_CHANNEL_HIERARCHY"" lh on case when gsv.vtweg = '10' then gsv.SOLD_TO else gsv.PRCTR end = lh.LOCATION_JOIN and lh.LOCATION_JOIN != ''#(lf)#(lf)where LEDGER = 'LOCAL'#(lf)and TYPE like 'SALE%'#(lf)and lh.REGION = 'Americas'#(lf)and lh.CHANNEL = 'Direct to Consumer'#(lf)and CREATION_WEEK >201899#(lf)group by CREATION_WEEK,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)gsv.PRCTR,#(lf)#(tab)#(tab)GENERIC#(lf)", Implementation="2.0"]),
#"Appended Query" = Table.Combine({#"Sales Query", #"Stock Query"}),
#"Grouped Rows" = Table.Group(#"Appended Query", {"WEEK_ID", "SITE", "GENERIC"}, {{"UNITS", each List.Sum([UNITS]), type nullable number}, {"NET_VALUE", each List.Sum([NET_VALUE]), type nullable number}, {"COST_OF_SALES", each List.Sum([COST_OF_SALES]), type nullable number}, {"GROSS_MARGIN", each List.Sum([GROSS_MARGIN]), type nullable number}, {"STOCK", each List.Sum([STOCK]), type nullable number}})
in
#"Grouped Rows"
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @TheCreepster1 ,
Don't append and merge at all.
Set your model up in the STAR SCHEMA structure, where your Sales and Inventory tables are the FACT tables, and any common fields (e.g. Location, Product etc.) are aggregated into DIMENSION tables that are then related to both fact tables.
You can then write measures that span both fact tables, as well as display data from both in visuals using the dimension table fields to maintain commonality between them.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/power-bi/guidance/star-schema
Another option would be to have your SQL query written on the source as a view, rather than being a native query from Power Query. Presuming both of your tables are on the same DB/server, your append/group steps should be able to be folded back to the source, which would be significantly quicker at performing these functions than Power Query.
Pete
Now accepting Kudos! If my post helped you, why not give it a thumbs-up?
Proud to be a Datanaut!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @TheCreepster1 ,
Don't append and merge at all.
Set your model up in the STAR SCHEMA structure, where your Sales and Inventory tables are the FACT tables, and any common fields (e.g. Location, Product etc.) are aggregated into DIMENSION tables that are then related to both fact tables.
You can then write measures that span both fact tables, as well as display data from both in visuals using the dimension table fields to maintain commonality between them.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/power-bi/guidance/star-schema
Another option would be to have your SQL query written on the source as a view, rather than being a native query from Power Query. Presuming both of your tables are on the same DB/server, your append/group steps should be able to be folded back to the source, which would be significantly quicker at performing these functions than Power Query.
Pete
Now accepting Kudos! If my post helped you, why not give it a thumbs-up?
Proud to be a Datanaut!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
Don't know why this didn't even cross my mind! Everything was set up to join as a star schema but I had it in my head I needed to smash the inventory and sales together for the end user. Unfortunately the two data sources are coming from different databases, hence the inability to do it in the SQL back end but I've managed to sort it through your first suggestion, thank you!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Try buffering the table to improve the performance.
Replace
#"Appended Query" = Table.Combine({#"Sales Query", #"Stock Query"}),with
#"Appended Query" = Table.Buffer(Table.Combine({#"Sales Query", #"Stock Query"})),Helpful resources

Join our Fabric User Panel
Share feedback directly with Fabric product managers, participate in targeted research studies and influence the Fabric roadmap.

Power BI Monthly Update - February 2026
Check out the February 2026 Power BI update to learn about new features.