- Power BI forums
- Updates
- News & Announcements
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Power Platform Integration - Better Together!
- Power Platform Integrations (Read-only)
- Power Platform and Dynamics 365 Integrations (Read-only)
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Community Connections & How-To Videos
- COVID-19 Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Data Stories Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- 2021 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2020 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2019 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- Events
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
- Community Blog
- Power BI Community Blog
- Custom Visuals Community Blog
- Community Support
- Community Accounts & Registration
- Using the Community
- Community Feedback
Register now to learn Fabric in free live sessions led by the best Microsoft experts. From Apr 16 to May 9, in English and Spanish.
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Re: Summarise table with condition
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Summarise table with condition
Hello
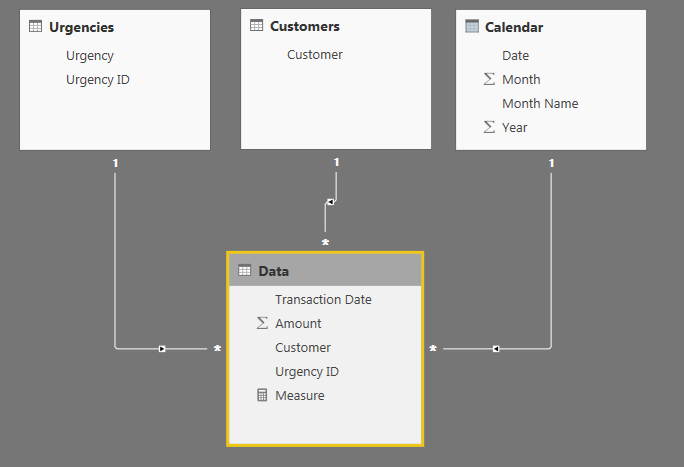
I have a transaction table with the following data:
| Transaction date | Amount | Urgency | Customer |
| 1-1-2017 | 50 | high | a |
| 30-5-2017 | 100 | medium | a |
| 30-9-2017 | 30 | low | a |
| 1-1-2018 | 45 | medium | a |
| 20-2-2018 | 55 | low | a |
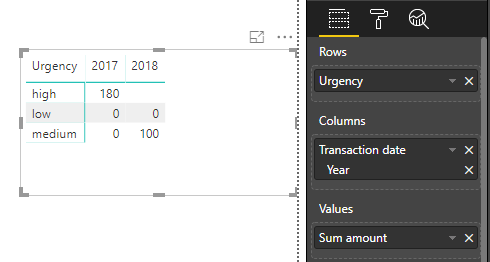
I want to summarise the data per year per urgency. Besides that each customer should be allocated to the transaction with the highest urgency within a year.
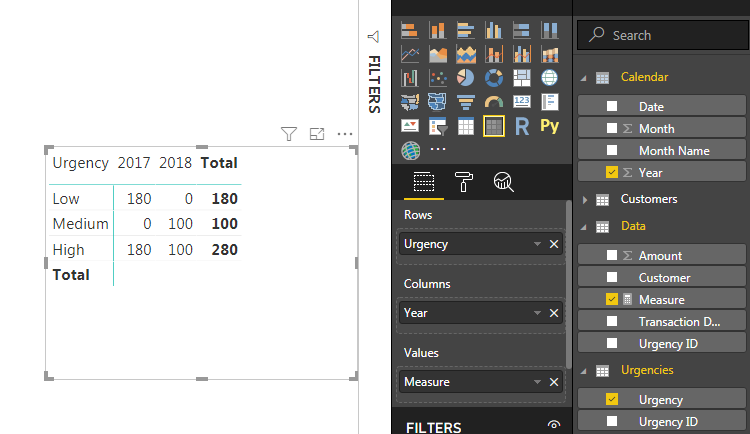
So finally I need to have:
| 2017 | 2018 | |
| High | 180 | 0 |
| Medium | 0 | 100 |
| Low | 0 | 0 |
I would appreciate your help!
Regards,
Jarno
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
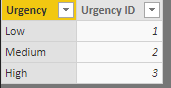
If you follow the Star Schema approach which LivioLanzo showed, then you can also use the below Calculated column HighestUrgencyID in Data table, and create a relationship between Urgency[UrgencyID] & Data[HighestUrgencyID]. This way your measure will be just SUM(Data[Amount]).
HighestUrgencyID =
VAR TransactionYear =
RELATED ( 'Calendar'[Year] )
VAR CurrentCustomer = 'Data'[Customer]
RETURN
CALCULATE (
MAX ( 'Data'[UrgencyID] ),
FILTER (
'Data',
'Data'[Customer] = CurrentCustomer
&& RELATED ( 'Calendar'[Year] ) = TransactionYear
)
)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @JarnoVisser
try like this:
Measure =
IF (
HASONEVALUE ( Urgencies[Urgency] ),
SUMX (
VALUES ( 'Calendar'[Year] ),
SUMX (
VALUES ( Customers[Customer] ),
IF (
CALCULATE (
MAX ( Data[Urgency ID] ),
ALL ( Urgencies )
) = SELECTEDVALUE ( Urgencies[Urgency ID] ),
CALCULATE (
SUM ( Data[Amount] ),
ALL ( Urgencies )
),
0
)
)
)
)
Did I answer your question correctly? Mark my answer as a solution!
Proud to be a Datanaut!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @JarnoVisser,
Add calculated columns:
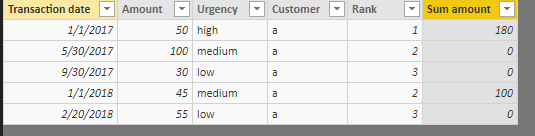
Rank =
IF ( Table2[Urgency] = "High", 1, IF ( Table2[Urgency] = "medium", 2, 3 ) )
Sum amount =
IF (
Table2[Rank]
= CALCULATE (
MIN ( Table2[Rank] ),
ALLEXCEPT ( Table2, Table2[Transaction date].[Year] )
),
CALCULATE (
SUM ( Table2[Amount] ),
ALLEXCEPT ( Table2, Table2[Transaction date].[Year] )
),
0
)
Use a Matrix to display data.
Best regards,
Yuliana Gu
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Yuliana,
Thank you for your reply!
It works fine for only one customer. But in my real data I have multiple customers like:
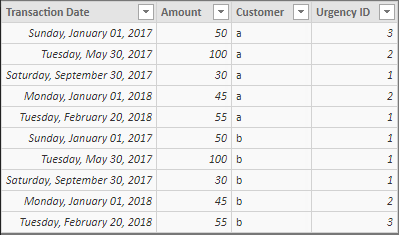
| Transaction date | Amount | Urgency | Customer |
| 1-1-2017 | 50 | high | a |
| 30-5-2017 | 100 | medium | a |
| 30-9-2017 | 30 | low | a |
| 1-1-2018 | 45 | medium | a |
| 20-2-2018 | 55 | low | a |
| 1-1-2017 | 50 | low | b |
| 30-5-2017 | 100 | low | b |
| 30-9-2017 | 30 | low | b |
| 1-1-2018 | 45 | medium | b |
| 20-2-2018 | 55 | high | b |
And with multiple customers it gives no amount for par example customer b in 2017. Do you have a solution for that?
Thanks in advance!
Kind regards,
Jarno
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
If you follow the Star Schema approach which LivioLanzo showed, then you can also use the below Calculated column HighestUrgencyID in Data table, and create a relationship between Urgency[UrgencyID] & Data[HighestUrgencyID]. This way your measure will be just SUM(Data[Amount]).
HighestUrgencyID =
VAR TransactionYear =
RELATED ( 'Calendar'[Year] )
VAR CurrentCustomer = 'Data'[Customer]
RETURN
CALCULATE (
MAX ( 'Data'[UrgencyID] ),
FILTER (
'Data',
'Data'[Customer] = CurrentCustomer
&& RELATED ( 'Calendar'[Year] ) = TransactionYear
)
)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thank you all! The most easy one even to verify is the solution of Akhil. The syntax of his solution should only be written as follows:
HighestUrgencyID =
VAR TransactionYear = RELATED ( 'Calendar'[Year] )
VAR CurrentCustomer = RELATED ('Dim'[Customer]
RETURN
CALCULATE (
MIN ( 'Data'[UrgencyID] ),
FILTER (
'Data',
'Data'[Customer] = CurrentCustomer
&& 'Data'[Year] ) = TransactionYear
)
)
Helpful resources

Microsoft Fabric Learn Together
Covering the world! 9:00-10:30 AM Sydney, 4:00-5:30 PM CET (Paris/Berlin), 7:00-8:30 PM Mexico City

Power BI Monthly Update - April 2024
Check out the April 2024 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 105 | |
| 94 | |
| 75 | |
| 63 | |
| 62 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 137 | |
| 105 | |
| 104 | |
| 80 | |
| 63 |