FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now! Learn more
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Replacement for Union in Direct Query
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Replacement for Union in Direct Query
Hello everyone,
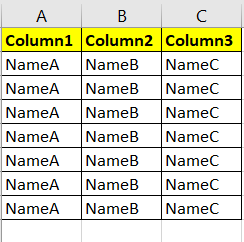
If I have this kind of table:
It is confirmed, all rows will have same value on each columns.
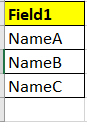
Initially I want to Transpose this data To be come simply like this :
With an addition of 1 column, so probably like this :
The ABC in column [Field] is actually can be the column name of 1st table, I just want to make it easier.
Is this possible with Direct Query Mode ?
At first I thought a UNION like this :
UNION(
SELECTCOLUMNS('Table', "Type", "A", "Description", 'Table'[Column1]),
SELECTCOLUMNS('Table', "Type", "B", "Description", 'Table'[Column2]),
SELECTCOLUMNS('Table', "Type", "C", "Description", 'Table'[Column3]),
But it turns out, this UNION forced me to switch to Import Mode. Any replacement trick to make this possible in Direct Query ?
Thanks
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Anonymous ,
According to the official document , Calculated tables aren't supported:
So, you could create the A, B, C three columns as three measures, and then use “union() “to achieve , as follows:
First: create three measures
Ameasure = MAX('Table'[A])BMeasure = MAX('Table'[B])Cmeasure = MAX('Table'[C])Then create new table:
newTable =
DISTINCT (
UNION (
SELECTCOLUMNS ( 'Table', "Type", "A", "Description", [Ameasure] ),
SELECTCOLUMNS ( 'Table', "Type", "B", "Description", [BMeasure] ),
SELECTCOLUMNS ( 'Table', "Type", "C", "Description", [Cmeasure] )
)
)
The final output is shown below:
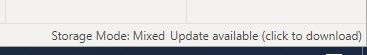
Last, If we create a virtual table with union(), the storage mode will change to mixed mode.
Best Regards,
Community Support Team_ Yalan Wu
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, @Anonymous
You could see my pbix file. Your data source is still in DQ mode. Since you created a virtual table with union(), it is mix(), which does not affect your data source itself.
Best Regards,
Community Support Team_ Yalan Wu
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Anonymous ,
According to the official document , Calculated tables aren't supported:
So, you could create the A, B, C three columns as three measures, and then use “union() “to achieve , as follows:
First: create three measures
Ameasure = MAX('Table'[A])BMeasure = MAX('Table'[B])Cmeasure = MAX('Table'[C])Then create new table:
newTable =
DISTINCT (
UNION (
SELECTCOLUMNS ( 'Table', "Type", "A", "Description", [Ameasure] ),
SELECTCOLUMNS ( 'Table', "Type", "B", "Description", [BMeasure] ),
SELECTCOLUMNS ( 'Table', "Type", "C", "Description", [Cmeasure] )
)
)
The final output is shown below:
Last, If we create a virtual table with union(), the storage mode will change to mixed mode.
Best Regards,
Community Support Team_ Yalan Wu
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
Thanks, but unfortunately I must use pure DIrect Query.
rgds,
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, @Anonymous
You could see my pbix file. Your data source is still in DQ mode. Since you created a virtual table with union(), it is mix(), which does not affect your data source itself.
Best Regards,
Community Support Team_ Yalan Wu
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
So, no TRANSPOSE.. and also no UNION...
No other tricks ? 😅
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@Anonymous , I was think of usin userealtionship with a table having distinct names (that can be as import mode table if needed)
But that depend of requirements https://radacad.com/userelationship-or-role-playing-dimension-dealing-with-inactive-relationships-in-power-bi
In this manner we can take total from three columns
also run time union in a measure, depend on need
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now!

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 40 | |
| 35 | |
| 34 | |
| 31 | |
| 28 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 136 | |
| 102 | |
| 68 | |
| 66 | |
| 58 |