- Power BI forums
- Updates
- News & Announcements
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Power Platform Integration - Better Together!
- Power Platform Integrations (Read-only)
- Power Platform and Dynamics 365 Integrations (Read-only)
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Community Connections & How-To Videos
- COVID-19 Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Data Stories Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- 2021 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2020 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2019 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- Events
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
- Community Blog
- Power BI Community Blog
- Custom Visuals Community Blog
- Community Support
- Community Accounts & Registration
- Using the Community
- Community Feedback
Register now to learn Fabric in free live sessions led by the best Microsoft experts. From Apr 16 to May 9, in English and Spanish.
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Re: Number to Binary
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Number to Binary
Is it possible to convert numbers to binary data in Power BI?
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I addition to my previous respons.
Some of the things I realized recently, is that:
an "if ... then ... else" statement with big chunks of code like above, is not required.
Thanks to concept of "Lazy Evaluation" in Power Query, you can just put in the code without if...then...else.
Intead, the choice is made later. In the example below: in the Result step.
So the inner part of the previous function (which is the actual function without documentation), can be rewritten as:
fnNBC = (input as anynonnull, base as number, optional outputlength as number) as any =>
let
// input = 10,
// base = 2,
// outputlength = null,
Base16 = "0123456789ABCDEF",
Base32 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ234567",
Base64 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/",
Lookups = List.Zip({{16,32,64},{Base16,Base32,Base64}}),
Lookup = Text.ToList(List.Last(List.Select(Lookups,each _{0} <= List.Max({16, base}))){1}),
InputToList = Text.ToList(input),
// This part will be executed if input is text:
Reversed = List.Reverse(InputToList),
BaseValues = List.Transform(Reversed, each List.PositionOf(Lookup,_)),
Indexed = List.Zip({BaseValues, {0..Text.Length(input)-1}}),
Powered = List.Transform(Indexed, each _{0}*Number.Power(base,_{1})),
Decimal = List.Sum(Powered),
// So far this part
// This part will be executed if input is not text:
Elements = 1+Number.RoundDown(Number.Log(input,base),0),
Powers = List.Transform(List.Reverse({0..Elements - 1}), each Number.Power(base,_)),
ResultString = List.Accumulate(Powers,
[Remainder = input,String = ""],
(c,p) => [Remainder = c[Remainder] - p * Number.RoundDown(c[Remainder] / p,0),
String = c[String] & Lookup{Number.RoundDown(c[Remainder]/p,0)}])[String],
PaddedResultString = if outputlength = null then ResultString else Text.PadStart(ResultString,outputlength,Lookup{0}),
// So far this part
Result = if input is text then Decimal else PaddedResultString
in
Result
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
In Power Query you can use Binary.FromText.
http://www.excelandpowerbi.com/?p=291
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
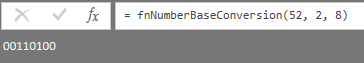
Thanks for the input. I tried using the approach to convert the number '52' to binary, but can't the expected output of 00110100. Is there another feature I'm missing to use numbers instead of hex or text?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I don't get it. All the binary functions seem to expect a binary value or text representing a binary value as the input. I don't see any function anywhere that converts base 10 to base 2.
Edit: seems a solution was presented while I was reading M documentation.
Did I answer your question? Mark my post as a solution!
Proud to be a Super User!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Still a reaction to your now-striked-through-text, just for better understanding:
in Power Query, "Binary" means: the binary representation of - for example - file contents, not a binary value as in 1001 = 9.
Of course: file contents are also a series of 0's and 1's, but they typically don't represent 1 (huge) decimal value. ![]()
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Got it. Thanks.
Did I answer your question? Mark my post as a solution!
Proud to be a Super User!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I know it is an old topic, but I just tried to reuse this code snippet, and it does not work for 0 and "0". Has anybody made that correction?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
It should work with "0", but not if the base is 32, which has no "0" in the 32 characters.
A small correction to have it work with 0:
in step "Elements" I added a List.Max formula, in order to supply a minimum of 1 as argument to Number.Log.
fnNBC = (input as anynonnull, base as number, optional outputlength as number) as any =>
let
// input = 10,
// base = 2,
// outputlength = null,
Base16 = "0123456789ABCDEF",
Base32 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ234567",
Base64 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/",
Lookups = List.Zip({{16,32,64},{Base16,Base32,Base64}}),
Lookup = Text.ToList(List.Last(List.Select(Lookups,each _{0} <= List.Max({16, base}))){1}),
InputToList = Text.ToList(input),
// This part will be executed if input is text:
Reversed = List.Reverse(InputToList),
BaseValues = List.Transform(Reversed, each List.PositionOf(Lookup,_)),
Indexed = List.Zip({BaseValues, {0..Text.Length(input)-1}}),
Powered = List.Transform(Indexed, each _{0}*Number.Power(base,_{1})),
Decimal = List.Sum(Powered),
// So far this part
// This part will be executed if input is not text:
Elements = 1+Number.RoundDown(Number.Log(List.Max({1,input}),base),0),
Powers = List.Transform(List.Reverse({0..Elements - 1}), each Number.Power(base,_)),
ResultString = List.Accumulate(Powers,
[Remainder = input,String = ""],
(c,p) => [Remainder = c[Remainder] - p * Number.RoundDown(c[Remainder] / p,0),
String = c[String] & Lookup{Number.RoundDown(c[Remainder]/p,0)}])[String],
PaddedResultString = if outputlength = null then ResultString else Text.PadStart(ResultString,outputlength,Lookup{0}),
// So far this part
Result = if input is text then Decimal else PaddedResultString
in
Result
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Some time ago I shared a great function on another forum.
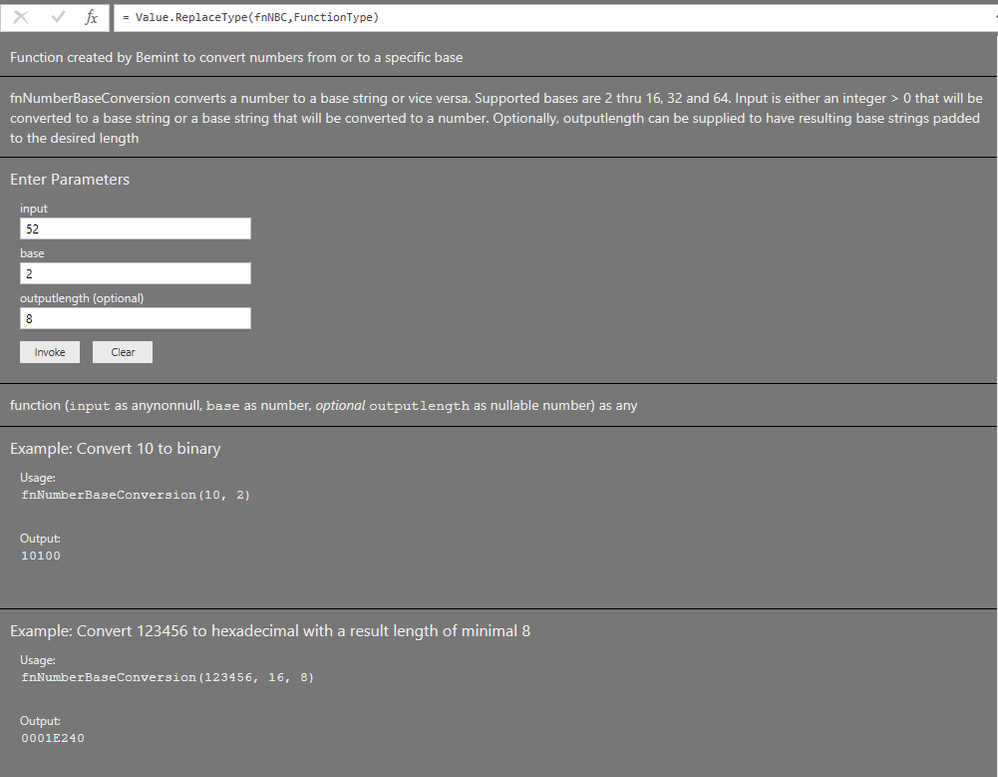
With this function - fnNumberBaseConversion - you can convert numbers to (almost) any base and vice versa.
Disclaimer: as far as I know, the function works fine, but I can't give any guarantees.
Screen shot with the parameters to get 00110100 from 52:
Result:
And the code, with complete documentation:
let
Documentation =
[Documentation.Category = "Custom Function",
Documentation.Description = "Function created by Bemint to convert numbers from or to a specific base",
Documentation.Examples = { [Description = "Convert 10 to binary",
Code = "fnNumberBaseConversion(10, 2)",
Result = "10100"],
[Description = "Convert 123456 to hexadecimal with a result length of minimal 8",
Code = "fnNumberBaseConversion(123456, 16, 8)",
Result = "0001E240"]},
Documentation.LongDescription =
"fnNumberBaseConversion converts a number to a base string or vice versa.
Supported bases are 2 thru 16, 32 and 64.
Input is either an integer > 0 that will be converted to a base string or a base string that will be converted to a number.
Optionally, outputlength can be supplied to have resulting base strings padded to the desired length"],
fnNBC = (input as anynonnull, base as number, optional outputlength as number) as any =>
let
// input = 10,
// base = 2,
// outputlength = null,
Base16 = "0123456789ABCDEF",
Base32 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ234567",
Base64 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/",
Lookups = List.Zip({{16,32,64},{Base16,Base32,Base64}}),
Lookup = Text.ToList(List.Last(List.Select(Lookups,each _{0} <= List.Max({16, base}))){1}),
InputToList = Text.ToList(input),
Result = if input is text
then
let
Reversed = List.Reverse(InputToList),
BaseValues = List.Transform(Reversed, each List.PositionOf(Lookup,_)),
Indexed = List.Zip({BaseValues, {0..Text.Length(input)-1}}),
Powered = List.Transform(Indexed, each _{0}*Number.Power(base,_{1})),
Decimal = List.Sum(Powered)
in
Decimal
else
let
Elements = 1+Number.RoundDown(Number.Log(input,base),0),
Powers = List.Transform(List.Reverse({0..Elements - 1}), each Number.Power(base,_)),
ResultString = List.Accumulate(Powers,
[Remainder = input,String = ""],
(c,p) => [Remainder = c[Remainder] - p * Number.RoundDown(c[Remainder] / p,0),
String = c[String] & Lookup{Number.RoundDown(c[Remainder]/p,0)}])[String],
PaddedResultString = if outputlength = null then ResultString else Text.PadStart(ResultString,outputlength,Lookup{0})
in
PaddedResultString
in
Result,
// Create FunctionType with metadata at function type level:
FunctionType = Type.ForFunction([ReturnType = type any, Parameters = [input = type anynonnull, base = type number, outputlength = type number]], 2) meta Documentation,
fnNumberBaseConversion = Value.ReplaceType(fnNBC,FunctionType)
in
fnNumberBaseConversion
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I addition to my previous respons.
Some of the things I realized recently, is that:
an "if ... then ... else" statement with big chunks of code like above, is not required.
Thanks to concept of "Lazy Evaluation" in Power Query, you can just put in the code without if...then...else.
Intead, the choice is made later. In the example below: in the Result step.
So the inner part of the previous function (which is the actual function without documentation), can be rewritten as:
fnNBC = (input as anynonnull, base as number, optional outputlength as number) as any =>
let
// input = 10,
// base = 2,
// outputlength = null,
Base16 = "0123456789ABCDEF",
Base32 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ234567",
Base64 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/",
Lookups = List.Zip({{16,32,64},{Base16,Base32,Base64}}),
Lookup = Text.ToList(List.Last(List.Select(Lookups,each _{0} <= List.Max({16, base}))){1}),
InputToList = Text.ToList(input),
// This part will be executed if input is text:
Reversed = List.Reverse(InputToList),
BaseValues = List.Transform(Reversed, each List.PositionOf(Lookup,_)),
Indexed = List.Zip({BaseValues, {0..Text.Length(input)-1}}),
Powered = List.Transform(Indexed, each _{0}*Number.Power(base,_{1})),
Decimal = List.Sum(Powered),
// So far this part
// This part will be executed if input is not text:
Elements = 1+Number.RoundDown(Number.Log(input,base),0),
Powers = List.Transform(List.Reverse({0..Elements - 1}), each Number.Power(base,_)),
ResultString = List.Accumulate(Powers,
[Remainder = input,String = ""],
(c,p) => [Remainder = c[Remainder] - p * Number.RoundDown(c[Remainder] / p,0),
String = c[String] & Lookup{Number.RoundDown(c[Remainder]/p,0)}])[String],
PaddedResultString = if outputlength = null then ResultString else Text.PadStart(ResultString,outputlength,Lookup{0}),
// So far this part
Result = if input is text then Decimal else PaddedResultString
in
Result
Helpful resources

Microsoft Fabric Learn Together
Covering the world! 9:00-10:30 AM Sydney, 4:00-5:30 PM CET (Paris/Berlin), 7:00-8:30 PM Mexico City

Power BI Monthly Update - April 2024
Check out the April 2024 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 96 | |
| 95 | |
| 82 | |
| 71 | |
| 64 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 115 | |
| 105 | |
| 95 | |
| 79 | |
| 72 |