FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now! Learn more
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Group by with gaps in data
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Group by with gaps in data
Hi
I cant think of a way to do this and hoping you can help.
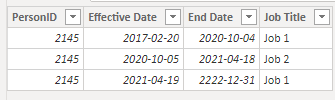
I have data that looks like this
| PersonID | Effective Date | End Date | Job Title |
| 2145 | 20/02/2017 | 30/04/2017 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 01/05/2017 | 14/09/2017 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 15/09/2017 | 01/10/2017 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 02/10/2017 | 11/01/2018 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 12/01/2018 | 31/07/2018 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 01/08/2018 | 14/09/2018 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 15/09/2018 | 14/09/2019 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 15/09/2019 | 04/10/2020 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 05/10/2020 | 18/04/2021 | Job 2 |
| 2145 | 19/04/2021 | 20/05/2021 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 21/05/2021 | 31/12/2222 | Job 1 |
I want to get it looking like this
| PersonID | Effective Date | End Date | Job Title |
| 2145 | 20/02/2017 | 04/10/2020 | Job 1 |
| 2145 | 05/10/2020 | 18/04/2021 | Job 2 |
| 2145 | 19/04/2021 | 31/12/2222 | Job 1 |
But every time i group by i'm only getting 2 rows because the job titles for job 1 are the same.
Any ideas? can this even be done?
Thanks
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @emmabrice ,
Here are the steps you can follow:
1. Create calculated column.
Index = RANKX('Table',[Effective Date],,ASC,Dense)Column =
var _lastrow=CALCULATE(MAX('Table'[Job Title]),FILTER(ALL('Table'),[Index]=EARLIER('Table'[Index])-1))
return
IF(_lastrow=[Job Title],0,1)Group = SUMX(FILTER(ALL('Table'),[Index]<=EARLIER('Table'[Index])),[Column])2. Create calculated table.
Table 2 =
var _summarize=
SUMMARIZE('Table',[PersonID],[Job Title],[Group],"1",MIN('Table'[Effective Date]),"2",MAX('Table'[End Date]))
return
SELECTCOLUMNS(_summarize,"PersonID",[PersonID],"Effective Date",[1],"End Date",[2],"Job Title",[Job Title])3. Result:
Best Regards,
Liu Yang
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @emmabrice ,
Here are the steps you can follow:
1. Create calculated column.
Index = RANKX('Table',[Effective Date],,ASC,Dense)Column =
var _lastrow=CALCULATE(MAX('Table'[Job Title]),FILTER(ALL('Table'),[Index]=EARLIER('Table'[Index])-1))
return
IF(_lastrow=[Job Title],0,1)Group = SUMX(FILTER(ALL('Table'),[Index]<=EARLIER('Table'[Index])),[Column])2. Create calculated table.
Table 2 =
var _summarize=
SUMMARIZE('Table',[PersonID],[Job Title],[Group],"1",MIN('Table'[Effective Date]),"2",MAX('Table'[End Date]))
return
SELECTCOLUMNS(_summarize,"PersonID",[PersonID],"Effective Date",[1],"End Date",[2],"Job Title",[Job Title])3. Result:
Best Regards,
Liu Yang
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
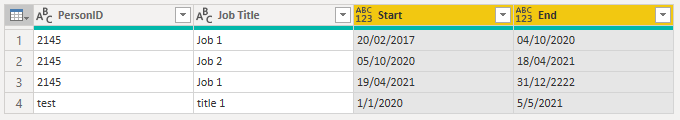
let
Source = Table.FromRows(Json.Document(Binary.Decompress(Binary.FromText("fZExCsMwDEWvUjwHpC9HxL5CrxCyFDIUCh3q+1O5rY0MST1ZvOcvIa9rEMwapiBMLCSMxYpoxdyK6/N2QdimrjKItVHMxPlUhTpq78DnqeIorAVqkQ5TxdFo6nKq1llTo33W41R1tKv5r1qpbeozuPDhAOoo0nevgp8qQ2p2tP6HenVIFThqG7CNiJ1BLfur1FRCa29Su5Z7eeyjGCm2RKUe3sXtDQ==", BinaryEncoding.Base64), Compression.Deflate)), let _t = ((type nullable text) meta [Serialized.Text = true]) in type table [PersonID = _t, #"Effective Date" = _t, #"End Date" = _t, #"Job Title" = _t]),
#"Grouped Rows" = Table.Group(Source, {"PersonID", "Job Title"}, {{"ar", each _}}, 0, (x,y) => Number.From(x[PersonID]<>y[PersonID] or x[Job Title]<>y[Job Title])),
Custom1 = Table.TransformColumns(#"Grouped Rows", {"ar", each let start=[Effective Date], end=[End Date] in [Start=start{0}, End=List.Last(end)]}),
#"Expanded ar" = Table.ExpandRecordColumn(Custom1, "ar", {"Start", "End"}, {"Start", "End"})
in
#"Expanded ar"| Thanks to the great efforts by MS engineers to simplify syntax of DAX! Most beginners are SUCCESSFULLY MISLED to think that they could easily master DAX; but it turns out that the intricacy of the most frequently used RANKX() is still way beyond their comprehension! |
DAX is simple, but NOT EASY! |
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now!

Power BI Monthly Update - November 2025
Check out the November 2025 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 59 | |
| 43 | |
| 42 | |
| 23 | |
| 17 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 190 | |
| 122 | |
| 96 | |
| 66 | |
| 47 |