FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now! Learn more
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Drawing trend line with categorical X axis [DAX]
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Drawing trend line with categorical X axis [DAX]
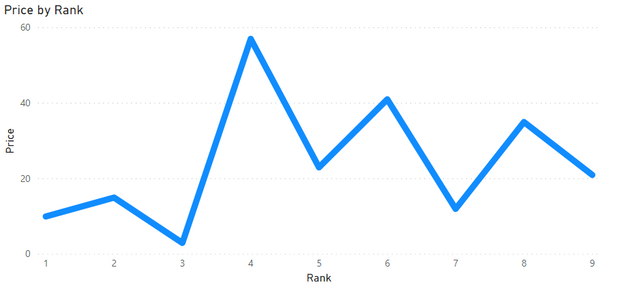
Hi, I have a simple table:
| Rank | Price |
| 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 15 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 57 |
| 5 | 23 |
| 6 | 41 |
| 7 | 12 |
| 8 | 35 |
| 9 | 21 |
I´d like to write a measure that returns a trend line.
I´ve read several posts but none helped.
- https://community.powerbi.com/t5/Desktop/Trend-line-x-axis/m-p/218665#M96973
- https://xxlbi.com/blog/simple-linear-regression-in-dax/
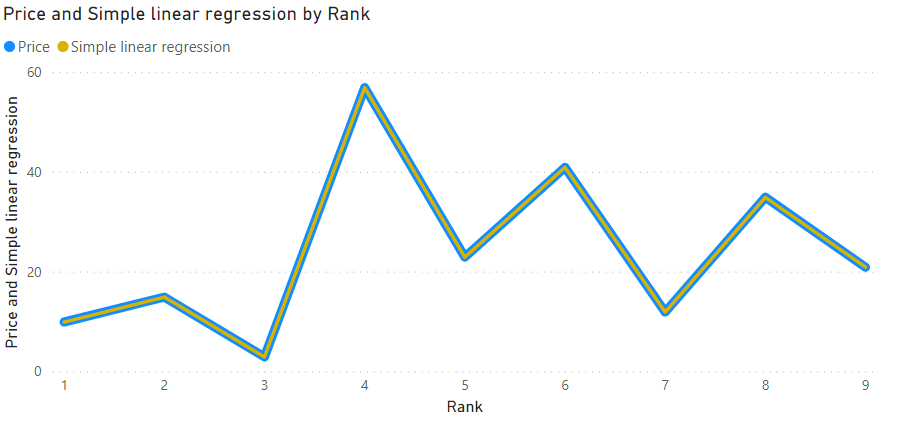
This measure:
Simple linear regression =
VAR Known =
FILTER (
SELECTCOLUMNS (
CALCULATETABLE( VALUES( 'Table'[Rank] ); ALLSELECTED ( 'Table'[Rank] ) );
"Known[X]"; 'Table'[Rank];
"Known[Y]"; SUM( 'Table'[Price] )
);
AND (
NOT ( ISBLANK ( Known[X] ) );
NOT ( ISBLANK ( Known[Y] ) )
)
)
VAR Count_Items =
COUNTROWS ( Known )
VAR Sum_X =
SUMX ( Known; Known[X] )
VAR Sum_X2 =
SUMX ( Known; Known[X] ^ 2 )
VAR Sum_Y =
SUMX ( Known; Known[Y] )
VAR Sum_XY =
SUMX ( Known; Known[X] * Known[Y] )
VAR Average_X =
AVERAGEX ( Known; Known[X] )
VAR Average_Y =
AVERAGEX ( Known; Known[Y] )
VAR Slope =
DIVIDE (
Count_Items * Sum_XY - Sum_X * Sum_Y;
Count_Items * Sum_X2 - Sum_X ^ 2
)
VAR Intercept =
Average_Y - Slope * Average_X
RETURN
SUMX (
DISTINCT ( 'Table'[Rank] );
Intercept + Slope * 'Table'[Rank]
)Returns the same line:
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @amitchandak, thanks for the tip, it helped me get the answer.
ALL(Known) does not work because you can´t use ALL with a table expression.
VAR Sum_X =
SUMX ( ALL ( Known ); Known[X] )
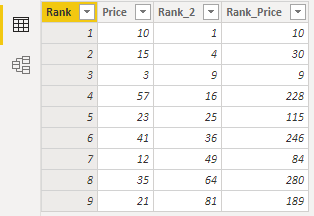
So I created two calculated columns:
Rank_2 = 'Table'[Rank] * 'Table'[Rank]
Rank_Price = 'Table'[Rank] * 'Table'[Price]
And used the measure with the table reference:
Simple linear regression =
VAR Count_Items =
CALCULATE( COUNTROWS ( 'Table' ); ALL( 'Table' ) )
VAR Sum_X =
SUMX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Rank] )
VAR Sum_X2 =
SUMX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Rank_2] )
VAR Sum_Y =
SUMX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Price] )
VAR Sum_XY =
SUMX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Rank_Price] )
VAR Average_X =
AVERAGEX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Rank] )
VAR Average_Y =
AVERAGEX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Price] )
VAR Slope =
DIVIDE (
Count_Items * Sum_XY - Sum_X * Sum_Y;
Count_Items * Sum_X2 - Sum_X ^ 2
)
VAR Intercept =
Average_Y - Slope * Average_X
RETURN
SUMX (
DISTINCT ( 'Table'[Rank] );
Intercept + Slope * 'Table'[Rank]
)
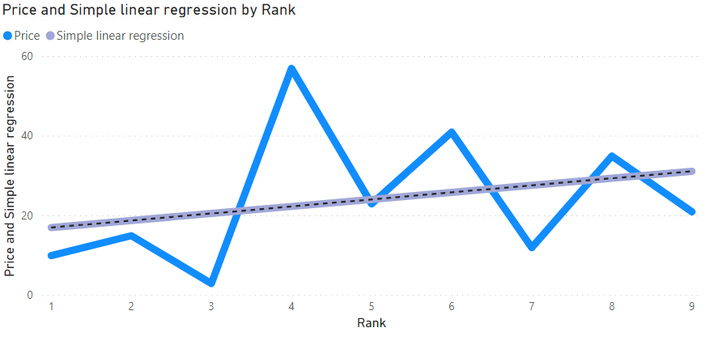
Edit: Corrected measure, now works ok.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@Anonymous . Check your formula, put values in table visual, and check. I think it taking row context.
Where possible put all(known) at place known and check
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @amitchandak, thanks for the tip, it helped me get the answer.
ALL(Known) does not work because you can´t use ALL with a table expression.
VAR Sum_X =
SUMX ( ALL ( Known ); Known[X] )
So I created two calculated columns:
Rank_2 = 'Table'[Rank] * 'Table'[Rank]
Rank_Price = 'Table'[Rank] * 'Table'[Price]
And used the measure with the table reference:
Simple linear regression =
VAR Count_Items =
CALCULATE( COUNTROWS ( 'Table' ); ALL( 'Table' ) )
VAR Sum_X =
SUMX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Rank] )
VAR Sum_X2 =
SUMX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Rank_2] )
VAR Sum_Y =
SUMX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Price] )
VAR Sum_XY =
SUMX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Rank_Price] )
VAR Average_X =
AVERAGEX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Rank] )
VAR Average_Y =
AVERAGEX ( ALL( 'Table' ); 'Table'[Price] )
VAR Slope =
DIVIDE (
Count_Items * Sum_XY - Sum_X * Sum_Y;
Count_Items * Sum_X2 - Sum_X ^ 2
)
VAR Intercept =
Average_Y - Slope * Average_X
RETURN
SUMX (
DISTINCT ( 'Table'[Rank] );
Intercept + Slope * 'Table'[Rank]
)

Edit: Corrected measure, now works ok.
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now!

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 40 | |
| 38 | |
| 36 | |
| 29 | |
| 28 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 127 | |
| 88 | |
| 78 | |
| 66 | |
| 65 |