FabCon is coming to Atlanta
Join us at FabCon Atlanta from March 16 - 20, 2026, for the ultimate Fabric, Power BI, AI and SQL community-led event. Save $200 with code FABCOMM.
Register now!- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- QuickViz Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Visual Calculations Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- TMDL Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now! Learn more
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Modifying quick measure YoY%
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Modifying quick measure YoY%
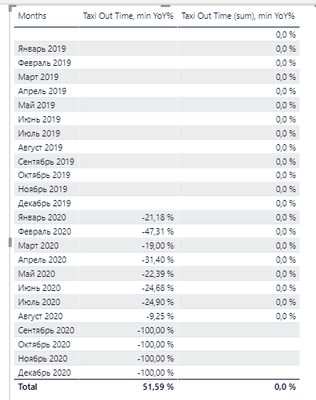
I tried to modify the quick measure (Year over year change). Original DAX looks like:
Taxi Out Time, min YoY% =
VAR __PREV_YEAR = CALCULATE(SUM('QAR data'[Taxi Out Time, min]), DATEADD('DATES'[DATE_FULL], -1, YEAR))
RETURN
DIVIDE(SUM('QAR data'[Taxi Out Time, min]) - __PREV_YEAR, __PREV_YEAR)
I decided to make some modification:
Taxi Out Time (sum), min YoY% =
VAR a = SUM('QAR data'[Taxi Out Time, min])
VAR prev_a = CALCULATE(a, SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR(DATES[DATE_FULL]))
RETURN
DIVIDE(a - prev_a, prev_a)
But new formula didn`t work well:
(the first column is a month name in Russian)
Please help to understand, what am I doing wrong?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Variables in DAX are CONSTANTS. Once calculated, they are NEVER re-calculated.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@Anonymous , Make share months are coming from Dates Table
This year = SUM('QAR data'[Taxi Out Time, min])
last Year = CALCULATE([This year], SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR(DATES[DATE_FULL]))
Change % =
DIVIDE([This year] - [last Year], [last Year])
Please provide your feedback comments and advice for new videos
Tutorial Series Dax Vs SQL Direct Query PBI Tips
Appreciate your Kudos.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, @Anonymous , the issue results from use of variable a in your measure; In fact, variables in DAX are NOT THAT VARIABLE as expected!
In DAX, variables are calculated within the scope in which they are written, and then the result of them is stored and used in the rest of the expression.
You might want to refer to an article on this subject for more details.
A straightforward way is to create a measure a = SUM('QAR data'[Taxi Out Time, min]), and you can reference it in another measure.
| Thanks to the great efforts by MS engineers to simplify syntax of DAX! Most beginners are SUCCESSFULLY MISLED to think that they could easily master DAX; but it turns out that the intricacy of the most frequently used RANKX() is still way beyond their comprehension! |
DAX is simple, but NOT EASY! |
Helpful resources

Power BI Dataviz World Championships
The Power BI Data Visualization World Championships is back! Get ahead of the game and start preparing now!

Power BI Monthly Update - November 2025
Check out the November 2025 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 20 | |
| 10 | |
| 9 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 32 | |
| 31 | |
| 18 | |
| 12 | |
| 11 |