Join the #PBI10 DataViz contest
Power BI is turning 10, and we’re marking the occasion with a special community challenge. Use your creativity to tell a story, uncover trends, or highlight something unexpected.
Get started- Power BI forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Contests Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- Notebook Gallery
- Translytical Task Flow Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas (read-only)
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
Join us for an expert-led overview of the tools and concepts you'll need to become a Certified Power BI Data Analyst and pass exam PL-300. Register now.
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Forecast
Hello everyone!
Here I am again needing help 😕
I have data from sensors, they measure the volume inside of tanks. I would like to forecast the volume for 1, 2, 3 and 4 weeks ahead.
I know that a line chart have the option of forecast, but I need the numbers in a table.
Please help!!!!!!!
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Antonio_Gomez ,
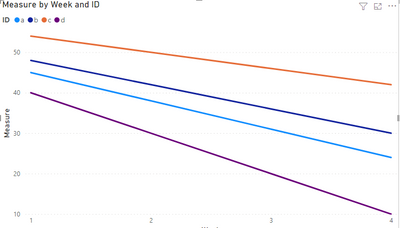
First I think you should calculate the [constant rate of use], then get the [remaining volume in the tank], and finally use a formula like the one below to get the forecast you want.
Measure =
SUM(FactTable[remaining volume in the tank])-SELECTEDVALUE('Week'[Week])*SUM(FactTable[constant rate of use])
Result:
Pbix in the end you can refer.
Best Regards
Community Support Team _ chenwu zhu
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @v-chenwuz-msft @amitchandak
I decided to do this:
Starting from the equation of the line Y = aX + b and the historical values I calculated for several days differents approximations. For example:
With today's value and yesterday's values I could construct one equation
Today volume = 890
Yesterday volume = 910
Today (X) = 0
Yesterday (X) = -1
a = (Y1 - Y2) / (X1 - X2)
So,
a = (890 - 910) / (0 - (-1))
b = Y - aX (isolated from the original equation)
And if I have the "a" from the last result; Y = today's volume and X = Today (X) = 0; I could have "b" and construct one equation.
Now, with this equation: Y = -20X + 890; I could predict for the day I wanted.
If I want to know the volume in 7 days, just put Y = (-20 * 7) + 890 = 750
I did this for several days in the past and always with today's reference
Y1 = Same as above
X1 = Same as above
Y2 = 915
X2 = -2 (the day before yesterday)
Y1 = Same as above
X1 = Same as above
Y2 = 930
X2 = -3
So, for each equation created taking into account the days in the past (in this example are 3; X = -1, X = -2 and X = -3), I forecast 7 days in the future Y = a(7) + b and average the three results to have the more approximated value.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@Antonio_Gomez , You can explore to bring data using R or Python connector and use forecasting by that R/Python
refer
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IP76UJ4nZ70
https://community.powerbi.com/t5/Desktop/Forecast-Using-AI-ML/td-p/1184505
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @amitchandak
I just realized that I used an incorrect term. I mean forecast, not predict. (And I edited the original post to avoid confusion)
For example, the product in the tank have a constant rate of use of 1 Lt/week.
So, if the remaining volume in the tank is 30 Lt, the forecast would show that in 1, 2, 3 and 4 weeks the volume will be 29, 28, 27 and 26 Lt.
There no need of use AI nor ML, things that I don't domine well 😞
.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Antonio_Gomez ,
First I think you should calculate the [constant rate of use], then get the [remaining volume in the tank], and finally use a formula like the one below to get the forecast you want.
Measure =
SUM(FactTable[remaining volume in the tank])-SELECTEDVALUE('Week'[Week])*SUM(FactTable[constant rate of use])
Result:
Pbix in the end you can refer.
Best Regards
Community Support Team _ chenwu zhu
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @v-chenwuz-msft @amitchandak
I decided to do this:
Starting from the equation of the line Y = aX + b and the historical values I calculated for several days differents approximations. For example:
With today's value and yesterday's values I could construct one equation
Today volume = 890
Yesterday volume = 910
Today (X) = 0
Yesterday (X) = -1
a = (Y1 - Y2) / (X1 - X2)
So,
a = (890 - 910) / (0 - (-1))
b = Y - aX (isolated from the original equation)
And if I have the "a" from the last result; Y = today's volume and X = Today (X) = 0; I could have "b" and construct one equation.
Now, with this equation: Y = -20X + 890; I could predict for the day I wanted.
If I want to know the volume in 7 days, just put Y = (-20 * 7) + 890 = 750
I did this for several days in the past and always with today's reference
Y1 = Same as above
X1 = Same as above
Y2 = 915
X2 = -2 (the day before yesterday)
Y1 = Same as above
X1 = Same as above
Y2 = 930
X2 = -3
So, for each equation created taking into account the days in the past (in this example are 3; X = -1, X = -2 and X = -3), I forecast 7 days in the future Y = a(7) + b and average the three results to have the more approximated value.
Helpful resources

Join our Fabric User Panel
This is your chance to engage directly with the engineering team behind Fabric and Power BI. Share your experiences and shape the future.

Power BI Monthly Update - June 2025
Check out the June 2025 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 65 | |
| 63 | |
| 52 | |
| 37 | |
| 36 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 79 | |
| 67 | |
| 60 | |
| 45 | |
| 45 |