- Power BI forums
- Updates
- News & Announcements
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Power Platform Integration - Better Together!
- Power Platform Integrations (Read-only)
- Power Platform and Dynamics 365 Integrations (Read-only)
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Community Connections & How-To Videos
- COVID-19 Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Data Stories Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- 2021 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2020 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2019 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- Events
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
- Community Blog
- Power BI Community Blog
- Custom Visuals Community Blog
- Community Support
- Community Accounts & Registration
- Using the Community
- Community Feedback
Register now to learn Fabric in free live sessions led by the best Microsoft experts. From Apr 16 to May 9, in English and Spanish.
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Re: No CACULATE challenge
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
No CACULATE challenge
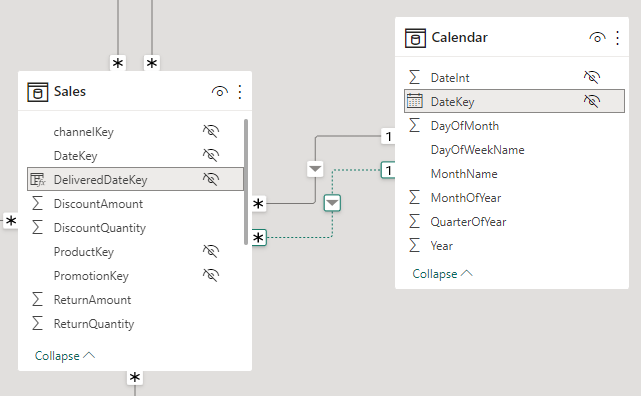
For those haters of CALCULATE like @Greg_Deckler, I challenge you to create a measure without CALCULATE that performs anywhere close to the same speed as this very simple measure that switches to an inactive relationship. It must also not break if a simple filter from any of the dimension tables is applied.
Sales Amount (Delivered) =
CALCULATE (
SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] ),
USERELATIONSHIP ( Sales[DeliveredDateKey], 'Calendar'[DateKey] )
)
Please use the attached file.
Report preview:
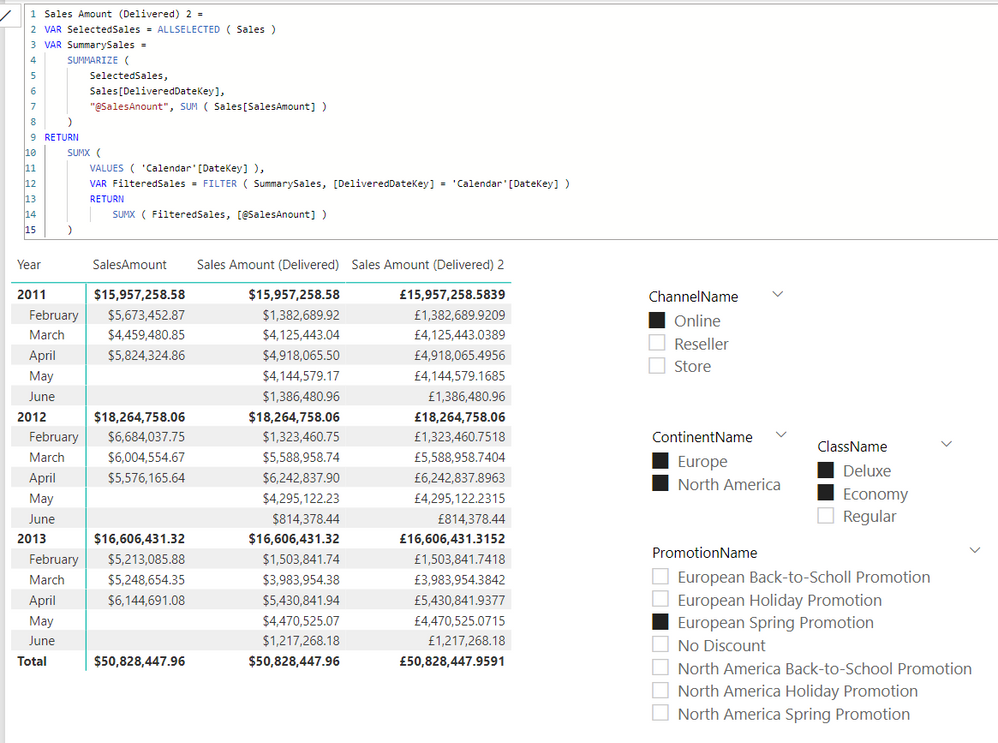
As expected, we can see that sales during periods without a discount promotion have products delivered in promotion months.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @AlexisOlson & @Greg_Deckler
This one uses neither CALCULATE nor CALCULATETABLE and performs faster than the original one
Sales Amount (Delivered) 2 =
VAR SelectedSales = ALLSELECTED ( Sales )
VAR SummarySales =
SUMMARIZE (
SelectedSales,
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"@SalesAnount", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] )
)
RETURN
SUMX (
VALUES ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] ),
VAR FilteredSales = FILTER ( SummarySales, [DeliveredDateKey] = 'Calendar'[DateKey] )
RETURN
SUMX ( FilteredSales, [@SalesAnount] )
)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
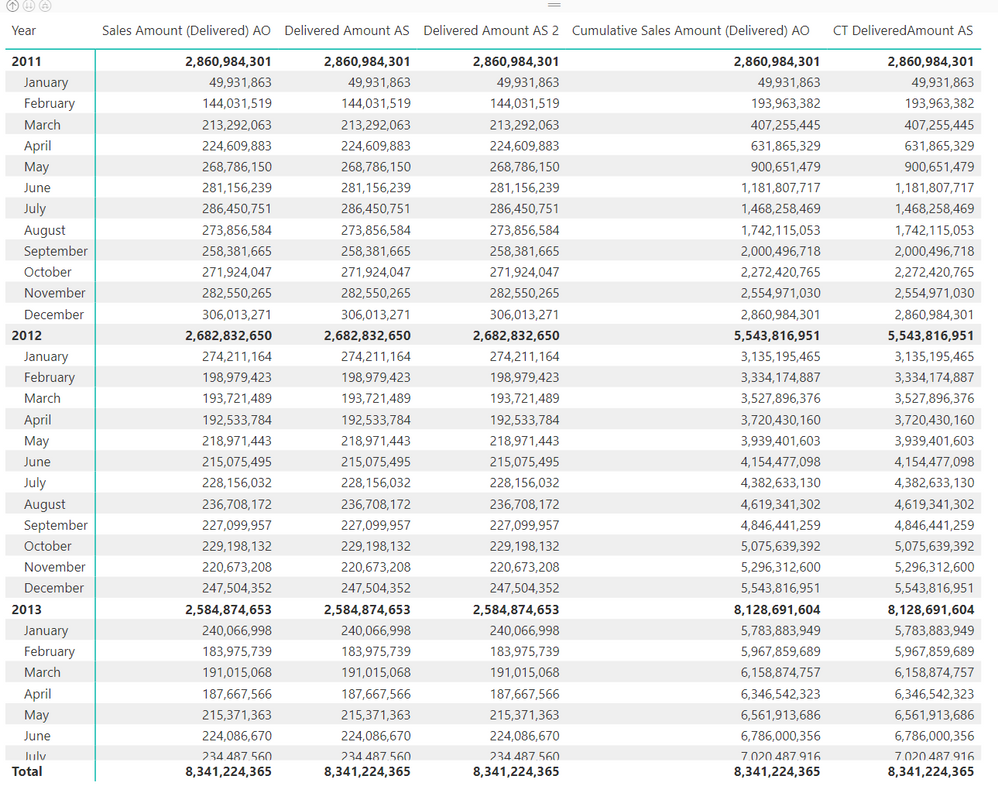
@AlexisOlson Good challenge! I am a Pro CALCULATE but recommend users not to stick with a single side.
Here are my solutions:
Solution 1 using INNERJOIN, performs in 40ms without any filter
Delivered Amount AS =
VAR Dates =
SELECTCOLUMNS (
VALUES ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] ),
"DeliveredDateKey", 'Calendar'[DateKey] & ""
)
VAR SalesByDelivery =
SELECTCOLUMNS (
SUMMARIZE (
ALLSELECTED ( Sales ),
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"Sum", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] )
),
"DeliveredDateKey", [DeliveredDateKey] & "",
"Sales", [Sum]
)
VAR Result =
SUMX (
NATURALINNERJOIN ( Dates, SalesByDelivery ),
[Sales]
)
RETURN
Result
Solution 2 using CONTAINSROW or the IN performs in 23 ms
Delivered Amount AS 2 =
VAR SalesByDeliveryDate =
SUMMARIZE (
ALL ( Sales ),
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"TotalSales", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] )
)
VAR CurrentYearRows =
FILTER (
SalesByDeliveryDate,
CONTAINSROW (
VALUES ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] ),
Sales[DeliveredDateKey]
)
)
VAR Result =
SUMX ( CurrentYearRows, [TotalSales] )
RETURN
Result
Cumulative Total - I added a YearMonth column in the Dates table, since we are not showing date level I decided to reduce granularity, takes about 50ms.
CT DeliveredAmount AS =
VAR SalesByDelivery =
SUMMARIZE (
ALL ( Sales ),
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"@TotalSales", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] ),
"@YearMonth", YEAR ( Sales[DeliveredDateKey] ) * 100 + MONTH ( Sales[DeliveredDateKey] )
)
VAR Result =
SUMX (
FILTER (
SalesByDelivery,
[@YearMonth] <= MAX ( 'Calendar'[YearMonth] )
),
[@TotalSales]
)
RETURN
Result
@tamerj1 I tried and your code and it returns incorrect subtotals.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I'm awarding the win to @tamerj1 for the original problem. It's about 20ms in testing on my machine instead of 10ms for mine but that's still super fast.
I'm awarding the win to @AntrikshSharma for the cumulative challenge since that solution works for subtotals as well.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@AlexisOlson Good challenge! I am a Pro CALCULATE but recommend users not to stick with a single side.
Here are my solutions:
Solution 1 using INNERJOIN, performs in 40ms without any filter
Delivered Amount AS =
VAR Dates =
SELECTCOLUMNS (
VALUES ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] ),
"DeliveredDateKey", 'Calendar'[DateKey] & ""
)
VAR SalesByDelivery =
SELECTCOLUMNS (
SUMMARIZE (
ALLSELECTED ( Sales ),
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"Sum", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] )
),
"DeliveredDateKey", [DeliveredDateKey] & "",
"Sales", [Sum]
)
VAR Result =
SUMX (
NATURALINNERJOIN ( Dates, SalesByDelivery ),
[Sales]
)
RETURN
Result
Solution 2 using CONTAINSROW or the IN performs in 23 ms
Delivered Amount AS 2 =
VAR SalesByDeliveryDate =
SUMMARIZE (
ALL ( Sales ),
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"TotalSales", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] )
)
VAR CurrentYearRows =
FILTER (
SalesByDeliveryDate,
CONTAINSROW (
VALUES ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] ),
Sales[DeliveredDateKey]
)
)
VAR Result =
SUMX ( CurrentYearRows, [TotalSales] )
RETURN
Result
Cumulative Total - I added a YearMonth column in the Dates table, since we are not showing date level I decided to reduce granularity, takes about 50ms.
CT DeliveredAmount AS =
VAR SalesByDelivery =
SUMMARIZE (
ALL ( Sales ),
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"@TotalSales", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] ),
"@YearMonth", YEAR ( Sales[DeliveredDateKey] ) * 100 + MONTH ( Sales[DeliveredDateKey] )
)
VAR Result =
SUMX (
FILTER (
SalesByDelivery,
[@YearMonth] <= MAX ( 'Calendar'[YearMonth] )
),
[@TotalSales]
)
RETURN
Result
@tamerj1 I tried and your code and it returns incorrect subtotals.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
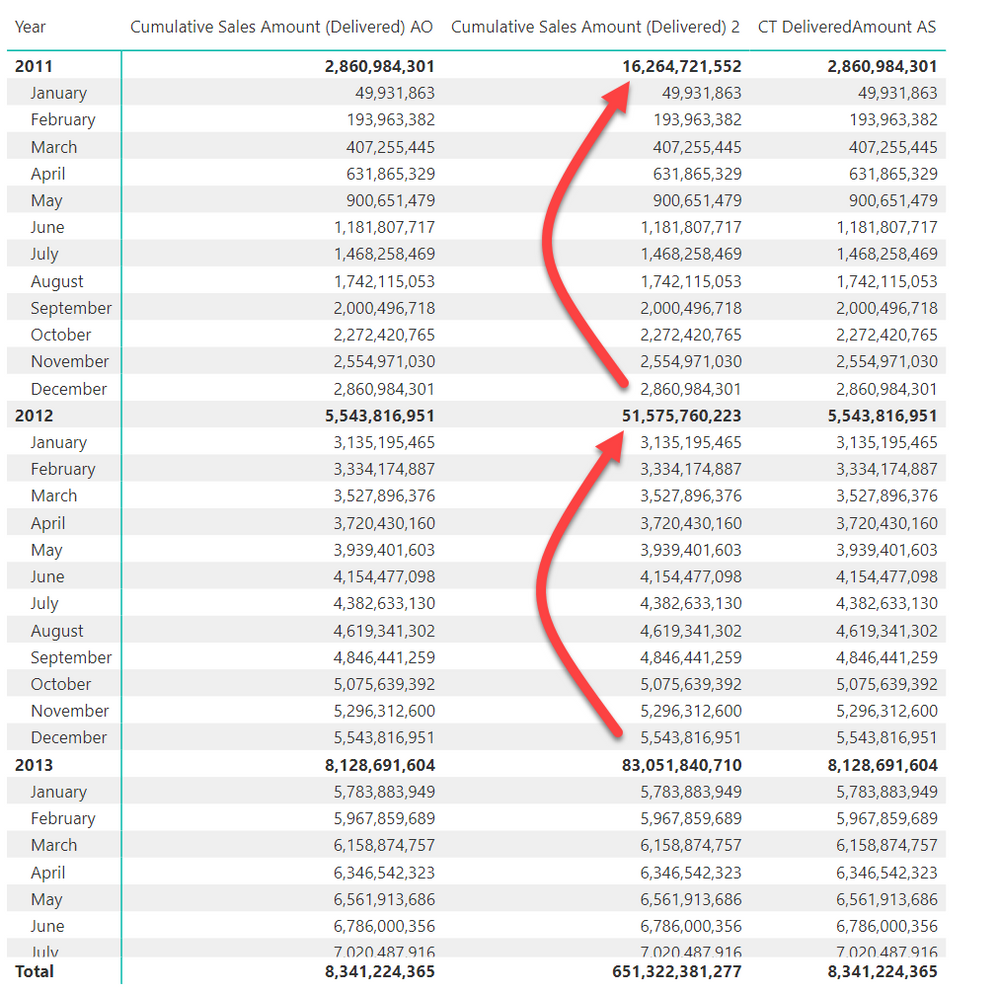
@AntrikshSharma
Yes you are right I've over looked that but this is an easy fix. The outer SUMX should have been a MAXX
Cumulative Sales Amount (Delivered) 2 =
VAR SelectedSales = ALLSELECTED ( Sales )
VAR SummarySales =
SUMMARIZE (
SelectedSales,
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"@SalesAnount", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] )
)
VAR SummaryDates =
SUMMARIZE (
'Calendar',
'Calendar'[Year],
'Calendar'[MonthName],
"@MaxDate", MAX ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] )
)
RETURN
MAXX (
SummaryDates,
VAR FilteredSales = FILTER ( SummarySales, [DeliveredDateKey] <= [@MaxDate] )
RETURN
SUMX ( FilteredSales, [@SalesAnount] )
)- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@tamerj1 Slick, way better than my revision in my video I made last night.
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Wow!
Thank you for mentioning me in your video ☺️
My name is Tamer Juma by the way and we are connected in LinkedIn actually you replied to my comments there couple of times.
Note: I fixed the wrong total by simply replacing the outer SUMX with MAXX
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@tamerj1 Yep, I saw that after the video went up. I posted the PBIX out on MicrosoftHatesGreg on github with the revised measure that corrects the subtotals. Absolutely, of course I'm going to mention you! You're one of the stars of the show! And nice to meet you Tamer Juma! Sorry, never put the two together before or my memory is failing me! But, it did let me work in the SwizzleStick420 joke!
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@AntrikshSharma Really impressive! If there is a restriction that you can't change the data model, then this slight tweak works just as well:
Cumulative Sales Amount (Delivered) AS rev =
VAR SalesByDelivery =
SUMMARIZE (
ALLSELECTED ( Sales ),
[DeliveredDateKey],
"@TotalSales", SUM ( [SalesAmount] ),
"@YearMonth", YEAR ( [DeliveredDateKey] ) * 100 + MONTH ( [DeliveredDateKey] )
)
VAR Result =
SUMX (
FILTER (
SalesByDelivery,
[@YearMonth] <= MAX ( 'Calendar'[Year] ) * 100 + MAX( 'Calendar'[MonthOfYear])
),
[@TotalSales]
)
RETURN
Result@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @AlexisOlson & @Greg_Deckler
This one uses neither CALCULATE nor CALCULATETABLE and performs faster than the original one
Sales Amount (Delivered) 2 =
VAR SelectedSales = ALLSELECTED ( Sales )
VAR SummarySales =
SUMMARIZE (
SelectedSales,
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"@SalesAnount", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] )
)
RETURN
SUMX (
VALUES ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] ),
VAR FilteredSales = FILTER ( SummarySales, [DeliveredDateKey] = 'Calendar'[DateKey] )
RETURN
SUMX ( FilteredSales, [@SalesAnount] )
)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
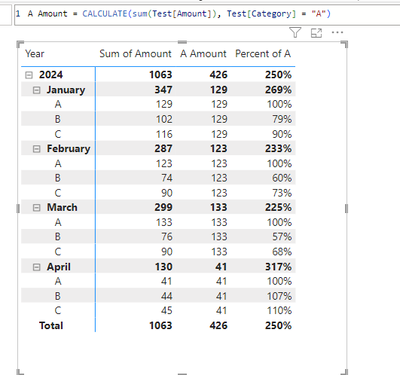
What's an easy no DAX to replace A Amount here. Basically, return the Amount of A in context to the visual regardless of category. So you can easily then calculate percent of A on any category, etc. I can't find a good way that isn't convoluted...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@Greg_Deckler I found Round 2 of these challenges and realized that addresses what is essentially what I am looking at here.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Sir, would you mind telling me how you can get sales for sameperiodlastyear without using calculate, knowing that the date table doesn't have date column, only year and quarters?I tried using filter() and max(), but it does not bring the correct values .
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@LuisMacedo Get your current year, maybe VAR __Year = MAX('Date'[Year]) then VAR __PY = __Year - 1, then filter ALL of your fact table where Year column = __PY? Hard to say exactly without knowing your data.
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Sales Amount (Delivered) NC =
VAR __Dates = SELECTCOLUMNS('Calendar',"DateKey",[DateKey])
VAR __Table = FILTER(ALLSELECTED('Sales'), [DeliveredDateKey] IN __Dates)
VAR __Result = SUMX(__Table, [SalesAmount])
RETURN
__ResultIn my testing the measures return within 50 milliseconds of one another.
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Nice!
Now try it without the slicer filtering and see how the performance compares. 🙂
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@AlexisOlson This one doesn't use CALCULATE either (LOL!) and is actually 3 times faster than the original measure from a DAX Query perspective.
NC3 =
VAR __Table = CALCULATETABLE('Sales', USERELATIONSHIP ( Sales[DeliveredDateKey], 'Calendar'[DateKey] ))
VAR __Result = SUMX(__Table, [SalesAmount])
RETURN
__Result@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@Greg_Deckler Ha! The performance of that is the same as my CALCULATE version in my testing.
For a final challenge, see if you can write a cumulative version without CALCULATE or CALCULATETABLE that refreshes in under 10 seconds with no slicer filtering. The CALCULATE version refreshes in about 0.2 sec, including all the overhead:
Cumulative Sales Amount (Delivered) =
VAR _MaxDate = MAX ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] )
VAR _Result =
CALCULATE (
SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] ),
USERELATIONSHIP ( Sales[DeliveredDateKey], 'Calendar'[DateKey] ),
ALL ( 'Calendar' ),
'Calendar'[DateKey] <= _MaxDate
)
RETURN
_Result
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@AlexisOlson
Here you go
Cumulative Sales Amount (Delivered) 2 =
VAR SelectedSales = ALLSELECTED ( Sales )
VAR SummarySales =
SUMMARIZE (
SelectedSales,
Sales[DeliveredDateKey],
"@SalesAnount", SUM ( Sales[SalesAmount] )
)
VAR SummaryDates =
SUMMARIZE (
'Calendar',
'Calendar'[Year],
'Calendar'[MonthName],
"@MaxDate", MAX ( 'Calendar'[DateKey] )
)
RETURN
SUMX (
SummaryDates,
VAR FilteredSales = FILTER ( SummarySales, [DeliveredDateKey] <= [@MaxDate] )
RETURN
SUMX ( FilteredSales, [@SalesAnount] )
)This is faster than yours. I guess @Greg_Deckler has a very good point 😉
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@tamerj1 One other thing, on a whim decided to replace SUMMARIZE with GROUPBY. SUMMARIZE is waaaaaayyyy more performant than GROUPBY. Like orders of magnitude more performant.
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
To be honest somehow I cheated 😅
I couldn't do that without context transition so I thought ok, SUMMARIZE can do that as well. Yes indeed GROUPBY does not perform context transition therefore would perform slower in this case.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@tamerj1 Wow! Super impressive! That is lightning fast!! I ran 10-15 tests and your version has DAX query timing that is on average 2-3 times faster than CALCULATE ( ~75 milliseconds versus ~200 milliseconds. Overall time was consistently 100 milliseconds faster. @Anonymous
The technique also works for the original problem and performs almost identically to the CALCULATE version.
NC4 =
VAR __SelectedSales = ALLSELECTED( 'Sales' )
VAR __SummarySales =
SUMMARIZE(
__SelectedSales,
[DeliveredDateKey],
"__SalesAmount", SUM( [SalesAmount] )
)
VAR __Dates = DISTINCT('Calendar'[DateKey])
VAR __Result =
SUMX( FILTER( __SummarySales, [DeliveredDateKey] IN __Dates), [__SalesAmount])
RETURNOnce again, CALCULATE goes down in defeat.
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
Helpful resources

Microsoft Fabric Learn Together
Covering the world! 9:00-10:30 AM Sydney, 4:00-5:30 PM CET (Paris/Berlin), 7:00-8:30 PM Mexico City

Power BI Monthly Update - April 2024
Check out the April 2024 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 40 | |
| 19 | |
| 17 | |
| 16 | |
| 15 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 50 | |
| 24 | |
| 21 | |
| 17 | |
| 16 |