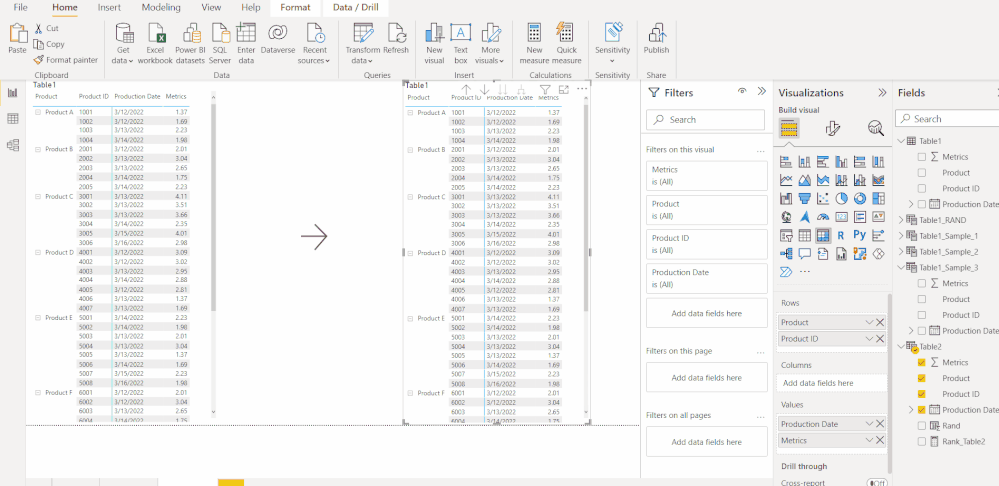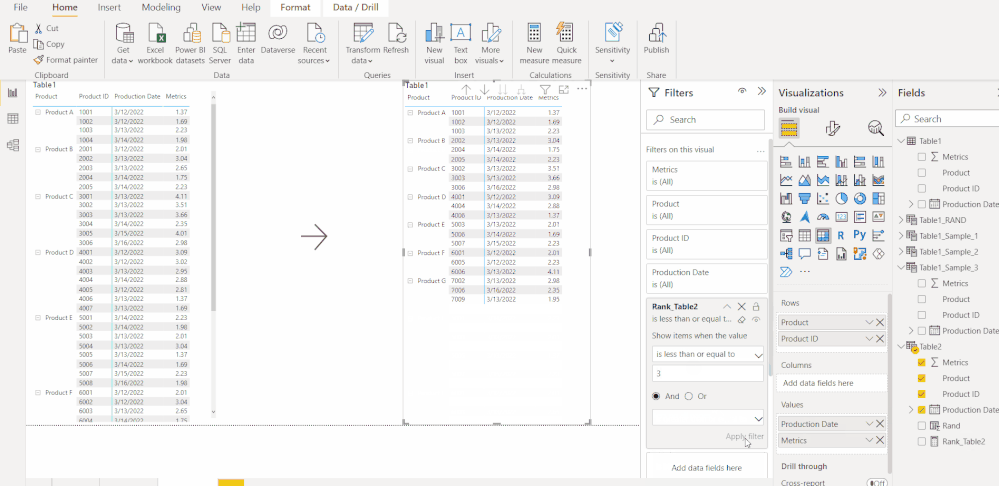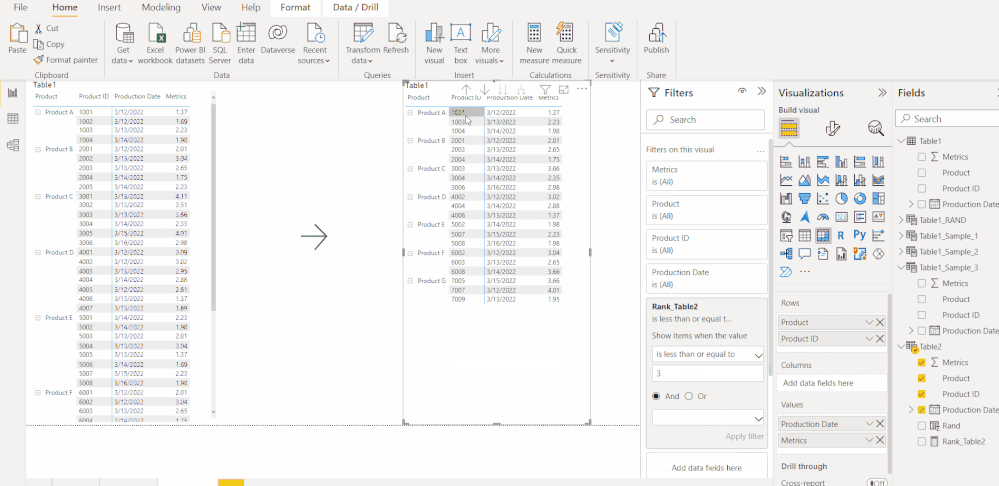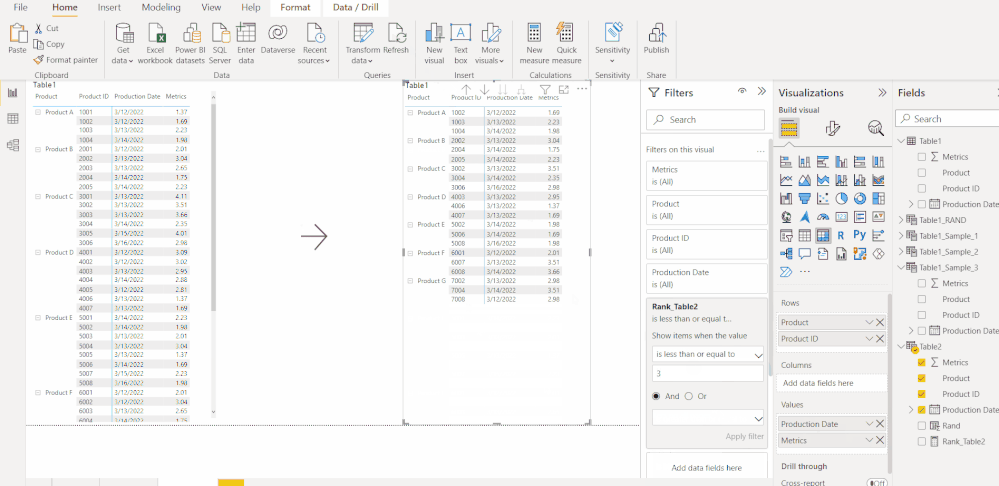
Go To
- Power BI forums
- Updates
- News & Announcements
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Power Platform Integration - Better Together!
- Power Platform Integrations (Read-only)
- Power Platform and Dynamics 365 Integrations (Read-only)
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Community Connections & How-To Videos
- COVID-19 Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Data Stories Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- 2021 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2020 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2019 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- Events
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
- Community Blog
- Power BI Community Blog
- Custom Visuals Community Blog
- Community Support
- Community Accounts & Registration
- Using the Community
- Community Feedback
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Register now to learn Fabric in free live sessions led by the best Microsoft experts. From Apr 16 to May 9, in English and Spanish.
- Power BI forums
- Community Blog
- Power BI Community Blog
Find articles, guides, information and community news
Options
- Mark all as New
- Mark all as Read
- Float this item to the top
- Subscribe
- Bookmark
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
Showing articles with label DAX.
Show all articles
Most Recent
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Labels:
Helpful resources
Featured Topics
Latest Articles
- Dynamic rollback of the previous N weeks of data
- Supercharge Your Visuals: Easy Conditional Formatt...
- The using of Cartesian products in many-to-many re...
- How to Filter similar Columns Based on Specific Co...
- Power BI Dynamic Date Filters: Automatically Updat...
- Enhanced Data Profiling in Power Query: GUI and Ta...
- How to use Tooltip to display breakdown data for a...
- Unveiling the Power of Lakehouse's SQL Analytics E...
- [DAX] Time Intelligence vs WINDOW vs OFFSET
- Display data in a fixed order and show data for th...
Latest Comments
- joseftantawi on: How to customize open-sourced custom visual.
- kalpeshdangar on: Creating Custom Calendars for Accurate Working Day...
- gwayne on: Embracing TMDL Functionalities in Power BI and Pre...
- jian123 on: Sharing Power Query tables
-
 Martin_D
on:
From the Desk of An Experienced Power BI Analyst
Martin_D
on:
From the Desk of An Experienced Power BI Analyst
-
 ibarrau
on:
[PowerQuery] Catch errors in a request http
ibarrau
on:
[PowerQuery] Catch errors in a request http
- Aditya07 on: How to import customised themes in Power BI - usin...
-
 Martin_D
on:
Currency Conversion in Power BI: Enabling Seamless...
Martin_D
on:
Currency Conversion in Power BI: Enabling Seamless...
-
 technolog
on:
Unveiling Top Products with categories: A Guide to...
technolog
on:
Unveiling Top Products with categories: A Guide to...
-
 Ritaf1983
on:
When Big Numbers Become Big Problems
Ritaf1983
on:
When Big Numbers Become Big Problems
-
How To
573 -
Tips & Tricks
526 -
Support insights
121 -
Events
107 -
DAX
66 -
Power BI
65 -
Opinion
64 -
Power Query
62 -
Power BI Desktop
40 -
Power BI Dev Camp
36 -
Roundup
31 -
Power BI Embedded
20 -
Time Intelligence
19 -
Tips&Tricks
18 -
PowerBI REST API
12 -
Power BI Service
8 -
Power Query Tips & Tricks
8 -
finance
8 -
Direct Query
7 -
Power Automate
6 -
Data Visualization
6 -
Python
6 -
Power BI REST API
6 -
Auto ML
6 -
financial reporting
6 -
Data Analysis
6 -
powerbi
5 -
service
5 -
Power BI PowerShell
5 -
Machine Learning
5 -
Featured User Group Leader
5 -
Dax studio
5 -
Income Statement
5 -
PowerShell
4 -
Desktop
4 -
Bookmarks
4 -
Group By
4 -
Line chart
4 -
community
4 -
RLS
4 -
M language
4 -
External tool
4 -
Paginated Reports
4 -
Power BI Goals
4 -
R
3 -
M Query
3 -
R visual
3 -
Webinar
3 -
CALCULATE
3 -
Reports
3 -
PowerApps
3 -
Data Science
3 -
Azure
3 -
Data model
3 -
Conditional Formatting
3 -
Visualisation
3 -
Administration
3 -
M code
3 -
SQL Server 2017 Express Edition
3 -
Visuals
3 -
R script
3 -
Aggregation
3 -
Dataflow
3 -
calendar
3 -
Gateways
3 -
slicers
2 -
SAP
2 -
index
2 -
RANKX
2 -
Integer
2 -
PBI Desktop
2 -
Date Dimension
2 -
Power BI Challenge
2 -
Query Parameter
2 -
Visualization
2 -
Tabular Editor
2 -
Date
2 -
SharePoint
2 -
Power BI Installation and Updates
2 -
How Things Work
2 -
troubleshooting
2 -
Date DIFF
2 -
Transform data
2 -
rank
2 -
ladataweb
2 -
Day of the Week
2 -
Tips and Tricks
2 -
Incremental Refresh
2 -
Query Plans
2 -
Power BI & Power Apps
2 -
Random numbers
2 -
Number Ranges
2 -
M
2 -
hierarchies
2 -
Power BI Anniversary
2 -
Language M
2 -
Custom Visual
2 -
VLOOKUP
2 -
pivot
2 -
calculated column
2 -
Power BI Premium Per user
2 -
inexact
2 -
Date Comparison
2 -
Split
2 -
Forecasting
2 -
REST API
2 -
Editor
2 -
Working with Non Standatd Periods
2 -
powerbi.tips
2 -
Custom function
2 -
Reverse
2 -
measure
2 -
Microsoft-flow
2 -
Paginated Report Builder
2 -
PUG
2 -
Custom Measures
2 -
Filtering
2 -
Row and column conversion
2 -
Python script
2 -
Nulls
2 -
DVW Analytics
2 -
Industrial App Store
2 -
Week
2 -
Date duration
2 -
parameter
2 -
Weekday Calendar
2 -
Support insights.
2 -
construct list
2 -
Formatting
2 -
Power Platform
2 -
Workday
2 -
external tools
2 -
Start of Week
1 -
Tips& Tricks
1 -
Training
1 -
Announcement
1 -
Features
1 -
domain
1 -
pbiviz
1 -
Color Map
1 -
Industrial
1 -
Weekday
1 -
Working Date
1 -
Space Issue
1 -
Emerson
1 -
Date Table
1 -
Cluster Analysis
1 -
Stacked Area Chart
1 -
union tables
1 -
Number
1 -
End of Week
1 -
Tips&Trick
1 -
deployment
1 -
ssrs traffic light indicators
1 -
SQL
1 -
trick
1 -
Scripts
1 -
Extract
1 -
Topper Color On Map
1 -
Historians
1 -
context transition
1 -
Custom textbox
1 -
OPC
1 -
Zabbix
1 -
Label: DAX
1 -
Business Analysis
1 -
Supporting Insight
1 -
rank value
1 -
Synapse
1 -
Premium Per User
1 -
GENERATESERIES
1 -
Workspace
1 -
Theme Colours
1 -
Text
1 -
Flow
1 -
Publish to Web
1 -
patch
1 -
Top Category Color
1 -
A&E data
1 -
Previous Order
1 -
Substring
1 -
Wonderware
1 -
Power M
1 -
Format DAX
1 -
Custom functions
1 -
accumulative
1 -
DAX&Power Query
1 -
Check
1 -
null value
1 -
Showcase
1 -
custom connector
1 -
Waterfall Chart
1 -
Power BI On-Premise Data Gateway
1 -
step by step
1 -
Top Brand Color on Map
1 -
Tutorial
1 -
Previous Date
1 -
XMLA End point
1 -
color reference
1 -
Date Time
1 -
Marker
1 -
Lineage
1 -
CSV file
1 -
conditional accumulative
1 -
Matrix Subtotal
1 -
Plotly package
1 -
refresh M language Python script Support Insights
1 -
Report Server
1 -
Audit Logs
1 -
analytics pane
1 -
mahak
1 -
pandas
1 -
Networkdays
1 -
Button
1 -
Dataset list
1 -
Keyboard Shortcuts
1 -
Fill Function
1 -
LOOKUPVALUE()
1 -
Tips &Tricks
1 -
Networkdays.Intl
1 -
Get row and column totals
1 -
Excel
1 -
Cumulative Totals
1 -
Report Theme
1 -
Bookmarking
1 -
oracle
1 -
Canvas Apps
1 -
total
1 -
Filter context
1 -
Difference between two dates
1 -
get data
1 -
OSI
1 -
Query format convert
1 -
ETL
1 -
Json files
1 -
Merge Rows
1 -
CONCATENATEX()
1 -
take over Datasets;
1 -
Azure AAD
1 -
Sameperiodlastyear
1 -
Office Theme
1 -
matrix
1 -
bar chart
1 -
Measures
1 -
powerbi argentina
1 -
Model Driven Apps
1 -
REMOVEFILTERS
1 -
XMLA endpoint
1 -
translations
1 -
OSI pi
1 -
Parquet
1 -
Change rows to columns
1 -
remove spaces
1 -
Week of the Day
1 -
Get latest sign-in data for each user
1 -
Governance
1 -
Fun
1 -
Power BI gateway
1 -
gateway
1 -
Elementary
1 -
Custom filters
1 -
Vertipaq Analyzer
1 -
powerbi cordoba
1 -
DIisconnected Tables
1 -
Sandbox
1 -
Honeywell
1 -
Combine queries
1 -
X axis at different granularity
1 -
ADLS
1 -
Primary Key
1 -
Microsoft 365 usage analytics data
1 -
Randomly filter
1 -
Power BI Show
1 -
Retail
1 -
Power BI Report Server
1 -
School
1 -
Cost-Benefit Analysis
1 -
ISV
1 -
Ties
1 -
unpivot
1 -
Practice Model
1 -
Continuous streak
1 -
ProcessVue
1 -
Create function
1 -
Table.Schema
1 -
Acknowledging
1 -
Postman
1 -
Text.ContainsAny
1 -
Tuesday
1 -
query
1 -
Dynamic Visuals
1 -
KPI
1 -
Intro
1 -
Icons
1 -
Issues
1 -
function
1 -
stacked column chart
1 -
ho
1 -
ABB
1 -
KNN algorithm
1 -
List.Zip
1 -
optimization
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Map Visual
1 -
Text.ContainsAll
1 -
Wednesday
1 -
API
1 -
Kingsley
1 -
Merge
1 -
variable
1 -
financial reporting hierarchies RLS
1 -
Featured Data Stories
1 -
MQTT
1 -
Custom Periods
1 -
Partial group
1 -
Reduce Size
1 -
FBL3N
1 -
Thursday
1 -
help
1 -
group
1 -
Scorecard
1 -
Json
1 -
Tops
1 -
Multivalued column
1 -
pipeline
1 -
Path
1 -
Yokogawa
1 -
Dynamic calculation
1 -
Data Wrangling
1 -
native folded query
1 -
transform table
1 -
UX
1 -
Cell content
1 -
General Ledger
1 -
Friday
1 -
Power Pivot
1 -
Quick Tips
1 -
data
1 -
PBIRS
1 -
Usage Metrics in Power BI
1 -
HR Analytics
1 -
keepfilters
1 -
Connect Data
1 -
Financial Year
1 -
Schneider
1 -
dynamically delete records
1 -
Copy Measures
1 -
Saturday
1 -
Table
1 -
Natural Query Language
1 -
Infographic
1 -
automation
1 -
Prediction
1 -
newworkspacepowerbi
1 -
Performance KPIs
1 -
Active Employee
1 -
Custom Date Range on Date Slicer
1 -
refresh error
1 -
PAS
1 -
certain duration
1 -
DA-100
1 -
bulk renaming of columns
1 -
Single Date Picker
1 -
Monday
1 -
PCS
1 -
Sunday
1 -
Q&A
1 -
Event
1 -
Custom Visuals
1 -
Free vs Pro
1 -
Format
1 -
Current Employees
1 -
date hierarchy
1 -
relationship
1 -
SIEMENS
1 -
Multiple Currency
1 -
Power BI Premium
1 -
On-premises data gateway
1 -
Binary
1 -
Power BI Connector for SAP
1 -
Field parameters
1 -
update
1 -
Slicer
1 -
Visual
1 -
forecast
1 -
Regression
1 -
CICD
1 -
sport statistics
1 -
Intelligent Plant
1 -
Circular dependency
1 -
GE
1 -
Exchange rate
1 -
Dendrogram
1 -
range of values
1 -
activity log
1 -
Decimal
1 -
Charticulator Challenge
1